A Guide to Predictive Analytics for Banks
Brian's Banking Blog
For years, banks have operated on experience, instinct, and rearview-mirror analysis. Predictive analytics changes the paradigm. It is the practice of leveraging proprietary data—both historical and real-time—to generate a clear, forward-looking view of market dynamics and portfolio risk.
This is not about generating more historical reports. It is about producing forward-looking intelligence that drives superior risk assessment, uncovers tangible growth opportunities, and builds the operational resilience required in a volatile economy. Predictive analytics is no longer a niche technology; it is a core strategic instrument for any modern banking leader.
Why Predictive Analytics Is Now Essential for Banking

The traditional playbook is insufficient in an environment defined by economic volatility, intense competition, and customers who expect proactive service. A more decisive, forward-thinking approach is required. Predictive analytics delivers the foresight necessary to navigate these conditions effectively.
This technology transforms a bank's data from a passive archive into an active strategic asset. Instead of merely analyzing what happened, leadership can forecast what is likely to happen next—and understand why. This capability allows an institution to stop reacting to market shifts and start proactively executing its strategy.
From Hindsight to Foresight
The fundamental shift is from analyzing yesterday's performance to anticipating tomorrow's outcomes. This empowers the entire institution to make more intelligent, faster decisions across every department. The financial implications are significant. The global market for predictive analytics in banking was valued at USD 3.63 billion and is projected to reach USD 19.61 billion by 2033.
This growth is fueled by tangible results. One major U.S. bank, for instance, reduced its default calculation time for 10 million loans from 96 hours to just 4 hours. You can explore the competitive advantages of predictive analytics for banks to understand the full scope of its impact.
This guide is designed for bank executives and directors. It cuts through technical jargon to provide a clear framework for converting data into measurable business value.
Consider the immediate, practical applications:
- Proactive Risk Management: Identifying loans with a high probability of default months before they manifest as delinquencies.
- Targeted Growth: Pinpointing commercial prospects most likely to require specific lending or treasury products in the near term.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Optimizing branch staffing and liquidity based on accurate forecasts of customer traffic and deposit flows.
For today's bank executive, the question is no longer if you should adopt predictive analytics, but how quickly you can integrate it to secure a competitive advantage. It is the definitive tool for translating data into decisive action.
Platforms like Visbanking’s Bank Intelligence and Action System (BIAS) are engineered to accelerate this journey. By unifying complex data sources into decision-ready intelligence, such platforms provide the foresight needed to anticipate market shifts rather than merely react to them.
Five High-Impact Applications in Your Bank

Predictive analytics transitions from a concept to a necessity when applied to core banking functions. For bank leaders, the value is not in the algorithms themselves but in the clear, measurable results that impact the bottom line.
Here are five areas where predictive analytics delivers the most significant return, shifting the focus from reactive problem-solving to strategic prevention.
Proactive Credit Risk Management
Traditional credit scoring provides a static, point-in-time snapshot, which is inadequate when economic conditions can shift rapidly. Predictive models analyze real-time transaction data, market shifts, and customer behavior to anticipate future risk. This is the difference between identifying a problem after it has occurred and preempting it entirely.
Consider your commercial real estate portfolio. A predictive model could fuse internal loan data with external signals like local vacancy rates or new UCC filings. It might flag a specific loan segment with a 15% higher probability of default—three quarters before it would appear in standard reports. This early warning provides the time to restructure loans or adjust reserves before the risk materializes on the balance sheet. In complex areas like trade finance, this foresight is critical, allowing banks to use Trade Finance Analytics to manage similar dynamic risks.
Intelligent Liquidity and Deposit Forecasting
Liquidity management, a banking fundamental, is often handled with overly cautious assumptions. Predictive analytics enables precision. By forecasting deposit inflows and outflows with high accuracy, a bank can operate a more dynamic and optimized balance sheet. It reveals the interplay between historical flows, seasonality, and customer behavior, enabling regulatory compliance without sacrificing profitability.
A practical example is predicting deposit runoff during a rising-rate environment. A model can identify which customers—based on tenure, average balance, and product usage—are most likely to chase higher yields. If the model forecasts a $50 million outflow from high-net-worth accounts over the next 90 days, leadership can launch a targeted CD campaign to retain those funds and protect core funding.
Enhanced Customer Growth and Retention
Acquiring a new customer is substantially more expensive than retaining an existing one. Predictive models act as a surveillance system, identifying at-risk customers with over 90% accuracy. They detect subtle behavioral changes, such as a drop in transaction frequency or declining balances, that signal potential attrition. This intelligence transforms relationship managers from reactive problem-solvers into a proactive retention force.
By forecasting which high-value customers are likely to leave, you can intervene with personalized offers or service calls, directly protecting your revenue base. Simultaneously, these models pinpoint the best cross-sell and upsell opportunities, ensuring your sales efforts are focused on customers with the highest propensity to buy.
The market for these tools is expanding rapidly for this reason, projected to grow from USD 3.84 billion to USD 4.64 billion in a single year. As early as 2018, 44% of financial institutions were already using predictive tools for retention because of their proven effectiveness.
Accelerated Sales and Prospecting
A banker's time is a bank's most valuable resource; it should not be wasted on low-probability outreach. Predictive analytics can build a dynamic, prioritized prospecting list that directs sales teams to businesses ready for a conversation. By combining external data—such as UCC filings, government contracts, or industry growth signals—with an ideal customer profile, a bank can systematically identify companies showing signs of needing commercial loans or treasury services.
For example, a model might flag a local manufacturing firm that recently filed three new UCCs and operates in a sector with 20% year-over-year growth. That company is no longer just a name on a list; it is a high-priority prospect with a demonstrated need. The efficiency and success rate of the sales team increase dramatically.
Strategic Talent Management
The same analytical logic applies to a bank's most critical asset: its people. Predictive models can analyze performance data, tenure, and engagement scores to forecast which employees are on a trajectory to become top performers or, conversely, are at risk of attrition. This gives HR and line managers the foresight to design retention strategies for key players and build development plans for rising stars, fostering a more stable and high-performing organization.
The following table outlines how these applications translate into tangible business impact.
Predictive Analytics Applications and Business Impact
| Banking Function | Predictive Application | Key Data Inputs | Measurable Business Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Credit | Early Warning System for Loan Defaults | Loan performance, transaction data, market indicators (e.g., UCC filings), economic data | Reduced charge-offs, optimized loan loss reserves, proactive risk mitigation |
| Liquidity | Deposit Runoff and Inflow Forecasting | Historical deposit flows, account holder behavior, interest rate sensitivity, seasonality | Optimized balance sheet, improved net interest margin, enhanced regulatory compliance |
| Customers | Customer Attrition (Churn) Prediction | Transaction frequency, balance changes, product usage, customer service interactions | Increased customer retention rates, higher lifetime value, protected revenue base |
| Sales | Prospect Prioritization | CRM data, external business data (e.g., firmographics, growth signals), ideal customer profiles | Higher sales conversion rates, shorter sales cycles, improved banker productivity |
| Talent | Employee Attrition and Performance Forecasting | HR data (tenure, role), performance reviews, engagement survey results, compensation data | Lower employee turnover, stronger leadership pipeline, improved organizational stability |
Ultimately, each of these applications depends on a robust data foundation. A platform like Visbanking’s BIAS connects disparate internal and external data sources, converting raw information into the actionable intelligence required to execute these strategies successfully.
Laying the Groundwork: Why Your Data Foundation is Everything

A predictive model is only as reliable as the data it consumes. The most sophisticated algorithm is not only useless but dangerous if it operates on incomplete or inaccurate data; it will simply produce flawed forecasts with greater speed.
The true starting point for predictive analytics is not code but clean, organized, and relevant information.
The most intensive work in any analytics project is unifying disparate data streams into a cohesive source of intelligence. This effort is substantial, but it is also the source of a significant competitive advantage. A complete, accurate picture cannot be derived from a single data source.
The Right Ingredients for Your Data Recipe
To generate useful predictive insights, internal knowledge must be blended with external market realities. Each data source provides a vital component of a larger picture that becomes clear only when all pieces are assembled.
The essential data categories include:
- Internal Core and CRM Data: This is the primary asset. Transaction histories, loan performance, deposit balances, and customer interactions represent the ground truth of customer behavior.
- Regulatory Filings: Public data, such as FDIC Call Reports and NCUA 5300 filings, provide industry benchmarks. They allow for the precise measurement of performance, risk, and strategy against peers.
- External Market and Economic Data: Information from UCC filings, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), and other commercial sources offers a real-time pulse on the economy. This data serves as an early warning system for market stress and opportunities not visible from an internal perspective.
A disciplined approach to information management is non-negotiable. Effective data governance in banking is what ensures the trustworthiness of all subsequent analysis.
Turning Raw Numbers into Real Intelligence
Simply possessing data is insufficient. The value is created through feature engineering—the process of converting raw data points into intelligent variables that can predict an outcome.
Consider how a veteran loan officer evaluates a commercial credit request. They do not merely look at a debt-to-income ratio. They mentally combine that figure with their knowledge of the local economy, the client's industry trends, and any recent liens. In essence, they are engineering features to make a more informed decision.
Predictive analytics systematizes and scales this expert-level judgment. It combines data points to create new signals that reveal risks or opportunities that would otherwise be missed.
For instance, a model could create a feature called "Business Cash Flow Stress" by combining several key inputs:
- Internal Data: A commercial client's average daily deposit balance has declined by 30% over the last six months.
- External Data: Two new UCC filings from suppliers have been registered against the business in the past 60 days.
- Market Data: The client's industry has contracted by 10%, according to the latest BLS data.
Individually, each data point is a warning sign. Combined by a model, they create a powerful, high-alert feature signaling a significantly elevated probability of default, long before a payment is missed.
This is precisely where a pre-unified data platform like Visbanking's BIAS provides a decisive advantage. By offering a production-grade feature store, it solves this foundational data challenge, saving a bank months or even years of development work and accelerating the path from raw data to actionable insight.
The Operational Engine Behind Predictive Banking
A predictive model is a high-performance engine; it has immense potential but requires an entire system built around it to function. MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) provides this operational framework for predictive analytics in banking.
For bank executives, the key takeaway is that deploying a model is the beginning, not the end. Lasting value is derived from a robust operational framework that manages and maintains these analytical assets throughout their lifecycle. Without it, you are operating a high-performance system without a support crew—a significant and unnecessary risk.
Operational rigor is no longer optional. According to McKinsey, 78% of organizations now use AI in at least one business function, up from 55% the previous year. Among banks with over $100 billion in assets, 75% are expected to fully integrate AI strategies by 2025 to combat cyber threats and refine risk assessment. You can discover more about how AI is accelerating banking trends and reshaping the competitive landscape.
Managing the Inevitable Model Drift
A predictive model's accuracy degrades over time. As soon as it is deployed, it begins to age. The economic conditions, customer behaviors, and market dynamics on which it was trained inevitably change. This natural decay in performance is known as concept drift, and ignoring it constitutes a major business risk.
Consider a credit risk model built before a period of rapid interest rate hikes. The patterns that predicted default in a low-rate environment are no longer reliable. New financial stressors emerge that the original model has never encountered.
An unmonitored model is a hidden liability. It continues to provide answers, but those answers become less accurate and more dangerous over time, leading to poor lending decisions and unexpected losses.
Effective MLOps is the solution. It establishes an automated system to continuously monitor a model’s performance against real-world outcomes. When its accuracy drops below a predefined threshold—for example, a 5% decrease in predicting loan delinquencies—the system flags it for retraining with fresh data.
From Technical Challenge to Strategic Asset
Building this operational infrastructure from scratch is a massive, expensive undertaking that requires specialized talent and significant investment. This is why modern data intelligence platforms are designed with MLOps as a core, integrated component, providing the entire quality control and maintenance system.
This includes critical components like a production-grade feature store. As noted earlier, features are the intelligent variables that fuel predictions. A well-managed feature store ensures these variables are consistent and reliable across all models, preventing the data inconsistencies that derail many analytics projects. You can explore this further in our guide on what a feature store is and its role in successful machine learning.
A solid operational engine transforms a complex technical problem into a managed, strategic asset. It provides the governance, reliability, and audit trail necessary to deploy predictive analytics with confidence, ensuring models deliver sustained performance and adapt to changing regulatory and market conditions.
By leveraging a platform with this infrastructure pre-built, a bank can bypass years of internal development and risk, focusing instead on acting on the intelligence the models provide.
Navigating Regulation and Ensuring Model Explainability
For a bank director, predictive analytics raises critical questions of governance and risk. It is insufficient for a model to be accurate; it must also be transparent. A prediction is only half the answer—the why is paramount.
Regulators, auditors, and internal risk committees will not accept "because the model said so" as a justification. If a model declines a loan application or flags a customer for risk, a clear, legally sound rationale compliant with Fair Lending laws is required. A "black box" model is an invitation for intense scrutiny and significant penalties.
The Mandate for Explainable AI
This requirement for transparency has made Explainable AI (XAI) a critical discipline. The principle is straightforward: every prediction must be traceable to the specific data points that produced it. This is how a bank proves its models are not only effective but also fair, ethical, and fully auditable.
Consider a commercial loan application denied by a predictive model. An explainable system provides a complete rationale, not just a verdict.
- Reason 1: Cash reserves have declined by 35% over the past two quarters, indicating potential liquidity stress.
- Reason 2: Two major suppliers recently filed UCCs, suggesting potential supply chain or payment issues.
- Reason 3: Key performance metrics are lagging behind peers in the same NAICS code, based on external benchmark data.
This level of detail transforms an algorithmic output into a clear, defensible business decision. It equips loan officers with the facts needed to communicate with applicants and provides the compliance team with the documentation required for regulatory review.
Building for Auditability and Trust
Meeting these regulatory demands requires a systematic approach. Modern data intelligence platforms are built for this reality, integrating auditability into every step. This is a core component of a sound model risk management framework, providing the structure to use advanced analytics without assuming undue risk.
An explainable model is a defensible model. When you can deconstruct and understand every prediction, you provide regulators with a clear audit trail and give your board the confidence that your analytics program is built on solid ground.
This transparency also builds internal trust. When lending teams, risk officers, and executives can see the logic behind a model's output, they are far more likely to adopt and rely on its insights.
Navigating the regulatory landscape is not a roadblock but a necessary component of implementing predictive analytics correctly. By prioritizing explainability, a bank can leverage powerful forecasting tools to drive performance with integrity.
Your Roadmap to Predictive Maturity
Implementing predictive analytics is a strategic journey, not a one-time project. The objective is to move beyond static dashboards and embed forward-looking intelligence into the daily decisions that drive performance. This requires a phased approach that prioritizes business value over technical complexity.
The most common and costly error is leading with technology instead of a clear business problem. The correct approach begins with a high-value question, such as, “How can we reduce commercial loan charge-offs by 15%?” or “How can we identify and retain our most profitable depositors?” A well-defined objective ensures that all resources are aligned with a measurable outcome.
This roadmap outlines a disciplined, three-phase journey from initial assessment to full integration, positioning your institution to compete in a data-driven future.
Phase 1: Foundational Assessment
Before building any model, an honest assessment of current capabilities is required. This phase focuses on identifying a high-impact, achievable initial project and aligning strategy with reality. The objective is to select one critical business problem that predictive analytics can solve and confirm that the necessary data is available.
This involves two primary actions:
Isolate a High-Impact Business Problem: Convene executive, lending, and operations teams to identify a significant pain point. An ideal candidate is a problem that is widely understood but unsolvable with current tools, such as predicting attrition among the top 5% of commercial clients or identifying local businesses that will require treasury services in the next six months.
Conduct a Data Asset Inventory: Once the problem is defined, map the required data. For a client attrition model, this would include CRM data, deposit and loan balances, transaction frequency, and potentially external signals like UCC filings. The key is to verify data access and quality before committing resources.
The most significant risk is assuming data is cleaner or more accessible than it is. A thorough inventory upfront prevents wasted effort and ensures the first project is properly resourced for success.
Phase 2: Pilot Program Launch
With a clear objective and validated data sources, the next step is a focused pilot program. This is not a research exercise but a time-boxed sprint with a clear, measurable goal. The aim is to prove value on a small scale, build internal support, and generate a tangible ROI to justify broader implementation.
A pilot to predict commercial client attrition, for example, requires a specific goal: “Identify at-risk commercial clients with 75% accuracy 90 days before account closure.” This level of specificity is critical. It establishes a clear benchmark for success and focuses the team on delivering a tool that relationship managers can use effectively.
The output of this phase should be a validated predictive model that generates a prioritized list of at-risk clients. This intelligence can be delivered directly to the front lines, empowering them with the foresight to conduct proactive outreach and retain revenue.
This flow chart illustrates how a model's prediction becomes a compliant, explainable action.
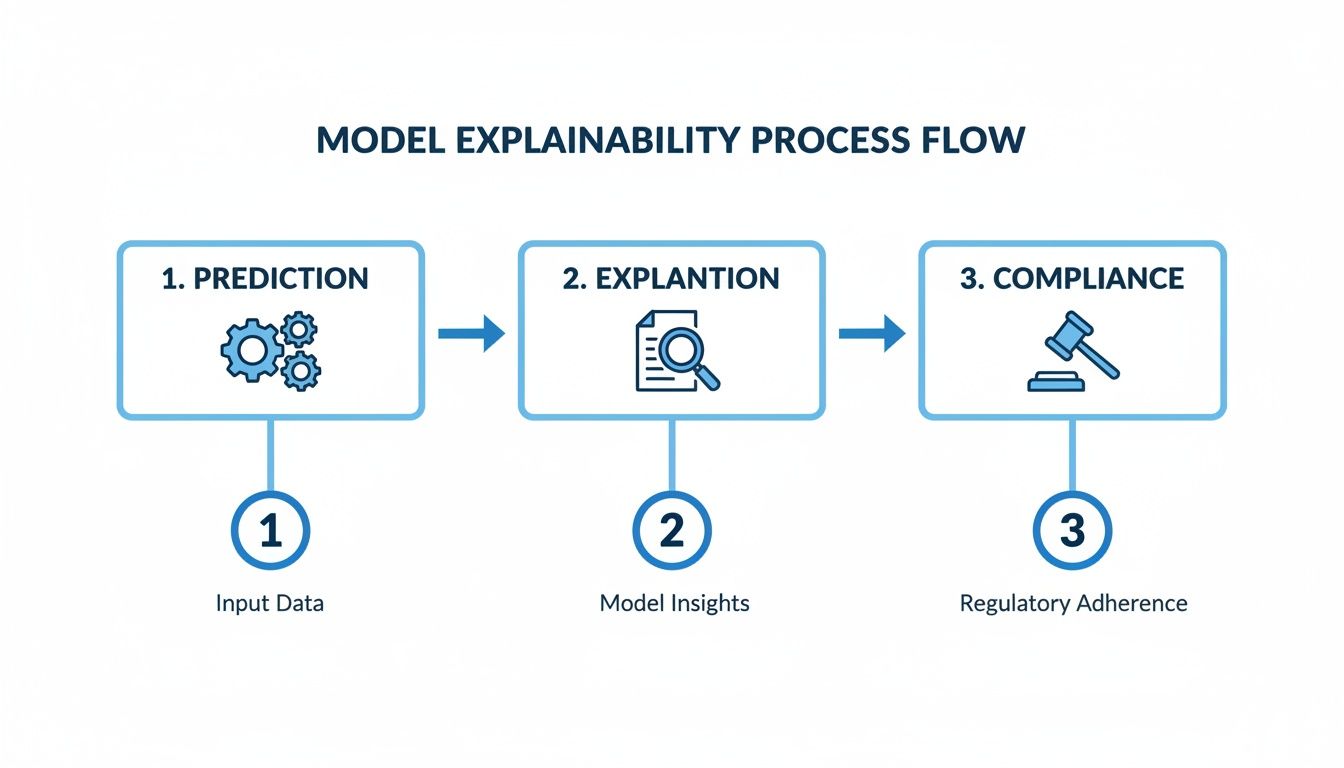
This is the critical path from a raw number to a decision that is fully documented and ready for regulatory review.
Phase 3: Scaling and Integration
Once the pilot has demonstrated clear value, it is time to scale. This final phase involves operationalizing the model and integrating its insights directly into the bank’s core workflows. The objective is to make predictive intelligence a seamless, automated part of daily operations.
This phase moves beyond generating standalone lists. Imagine an attrition risk score appearing automatically within a client’s CRM profile, alongside the top three reasons for the risk flag. This transforms the insight from something a banker must seek out to an alert they cannot miss.
Scaling also involves identifying new business lines where the same predictive architecture can be applied. A successful credit risk model for one portfolio can be adapted for another, leveraging the same data foundation and MLOps framework. A strategic partner with pre-built infrastructure can serve as a significant accelerator in this phase, enabling the rapid and efficient replication of successful initiatives. This systematic journey moves an institution from merely observing data to taking decisive, data-driven action.
Your journey to predictive maturity is a strategic imperative. At Visbanking, our BIAS platform provides the unified data, proven models, and operational infrastructure to accelerate every phase of this roadmap. Move from analysis to action and see how your institution stacks up.
Explore our data and benchmark your bank’s performance at https://www.visbanking.com.
Similar Articles

Visbanking Blog
Banking Data Analytics: Turning Information Into Profit

Visbanking Blog
Revolutionize Your Banking Operations with Data-Driven Insights from BIAS

Visbanking Blog
BIAS: A New Dawn in Banking Decision-Making

Visbanking Blog
Make More Informed Decisions with BIAS, the Data-Driven Banking Solution

Visbanking Blog
Fastest Growing Banks: Who's Winning the Asset Race?

Visbanking Blog
Revolutionize Your Bank's Performance with BIAS: Unlocking the Future of Visual Banking Data

Visbanking Blog
BIAS: The Smart Choice for Banking Intelligence and Action

Visbanking Blog
BIAS: The Smart Choice for Banking Intelligence and Action

Visbanking Blog
🔥 'Data is the new oil.'

Visbanking Blog