Master Banking Regulatory Compliance Strategies Today
Brian's Banking Blog
The New Reality of Banking Regulatory Compliance

The financial world has changed significantly regarding regulatory compliance since 2008. Reactive compliance is no longer sufficient. Today's financial institutions must proactively manage a complex and constantly changing regulatory landscape. This presents serious challenges, even for seasoned banking professionals. Forward-thinking institutions are adapting to this shift.
Proactive Compliance: Turning Challenges into Opportunities
This shift from reactive to proactive compliance management is changing banking operations globally. Instead of seeing compliance as a cost center, leading banks are turning regulatory requirements into competitive advantages.
For example, investing in robust compliance systems helps build trust with customers and investors. This strengthens their market position. This proactive approach not only reduces risk but also builds a culture of ethical and responsible banking.
The increased regulatory oversight isn't random. The banking sector has seen major regulatory changes over the past few decades, especially after 2008.
The global financial crisis resulted in stricter regulations like the Basel III standards, designed to improve capital adequacy and financial stability. By 2019, banks were implementing these standards, many significantly increasing their capital reserves. The Basel III framework, for instance, requires a minimum common equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratio of 4.5% and a total capital ratio of 8%.
This move toward stricter regulations is a global phenomenon, with organizations like the Financial Stability Board (FSB) and the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision playing key roles. For more information on banking regulatory trends, check out this resource: Learn more about bank regulatory trends. This increased scrutiny demands a proactive approach.
Navigating Global Regulatory Coordination
The increasing interconnectedness of the global financial system means regulatory coordination is more important than ever. This directly affects daily operations for institutions working across multiple jurisdictions.
Consider a bank with branches in several countries. Each jurisdiction might have its own specific regulations, resulting in complicated compliance requirements. Staying ahead requires a deep understanding of evolving regulations. The following resource offers valuable insights: digital regulations and compliance.
Understanding and anticipating regulatory changes across different jurisdictions is crucial for success in modern banking. The new reality of banking regulatory compliance requires changes in mindset, operations, and technology. Institutions that embrace this change will not just survive, but thrive.
The True Price Tag of Banking Compliance Excellence
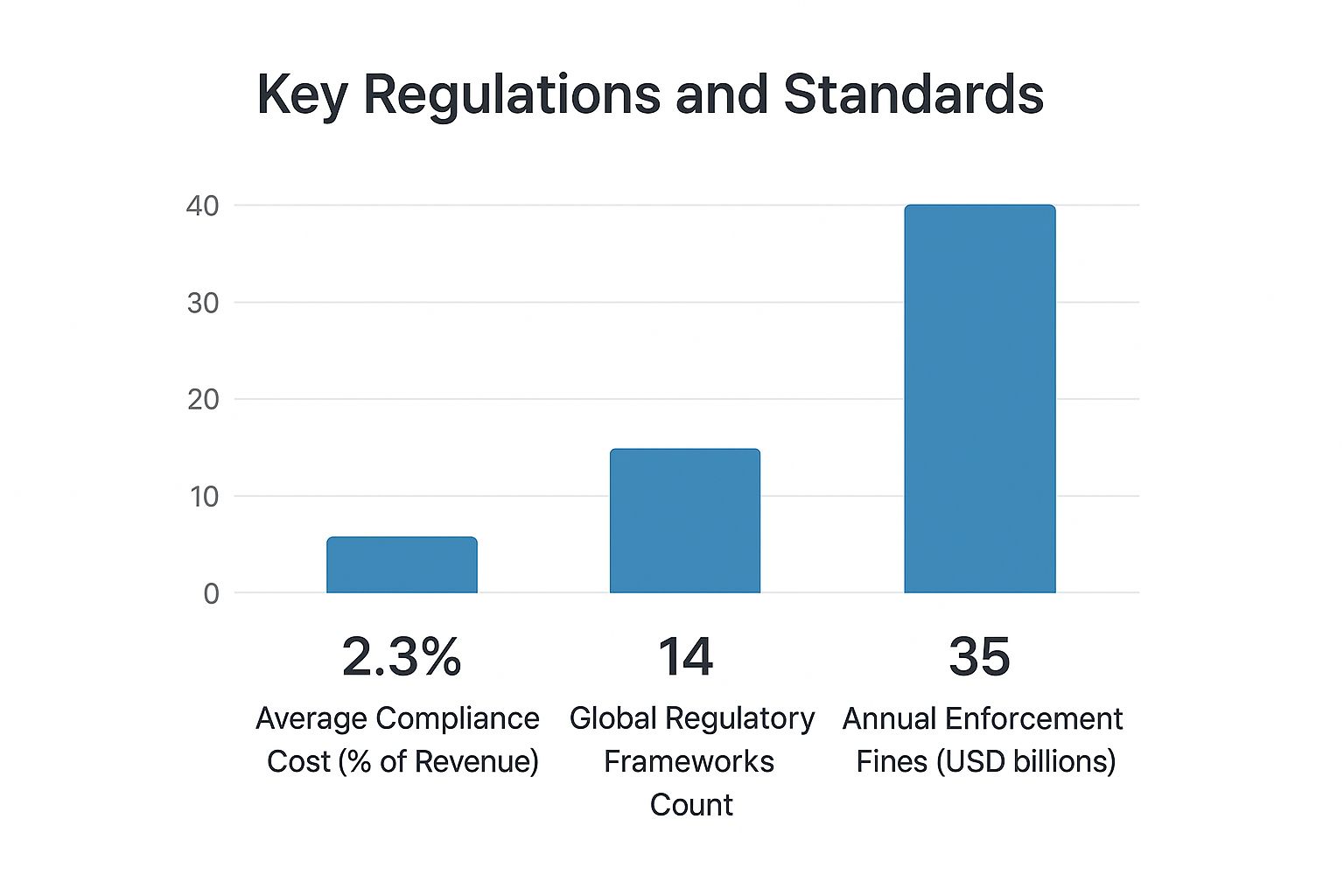
This infographic illustrates the average compliance costs for banks as a percentage of revenue. It also shows the sheer number of global regulatory frameworks and the hefty total of annual enforcement fines. These combined figures paint a clear picture of the significant financial impact of staying compliant.
Maintaining regulatory compliance in banking isn't just a matter of ticking boxes; it’s a considerable investment. Beyond the obvious expenses like fines and penalties, there's a much larger financial impact affecting a bank's bottom line. This includes expenses ranging from specialized personnel and continuous training to the ever-evolving need for updated technology.
Understanding the Hidden Costs of Compliance
Think about the cost of personnel, for example. Effective compliance teams need skilled professionals who are deeply familiar with the constantly changing regulations. This means not only competitive salaries but also the ongoing cost of professional development to keep their knowledge current.
Technology also plays a vital role in modern banking compliance. Investing in and maintaining essential compliance software, efficient data management systems, and robust cybersecurity infrastructure represents a substantial portion of any bank's budget. How to master regulatory compliance for banks. Furthermore, regulations change frequently, and technology must adapt, adding to the expense.
In recent years, the cost of compliance has become a major concern for banks. The sheer volume and complexity of regulations have pushed expenses higher for all financial institutions. A Deloitte study found that the average bank allocates roughly 15% of its annual budget to compliance, including personnel, technology, and consulting services. Find more detailed statistics here. Regulatory bodies like the Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions (OSFI) have increased their focus on compliance management, further emphasizing the need for strong frameworks. This can be particularly difficult for smaller institutions that may have limited resources for compliance technology compared to their larger counterparts.
The following table provides a detailed breakdown of these compliance costs across different bank sizes:
"Compliance Cost Breakdown for Financial Institutions" A detailed breakdown of average compliance expenses across different bank sizes.
| Expense Category | Small Banks (<$10B assets) | Mid-Size Banks ($10B-$50B) | Large Banks (>$50B) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personnel | 4% of annual budget | 6% of annual budget | 8% of annual budget |
| Technology | 3% of annual budget | 5% of annual budget | 7% of annual budget |
| Consulting & Legal | 2% of annual budget | 3% of annual budget | 4% of annual budget |
| Total Compliance Costs | 9% of annual budget | 14% of annual budget | 19% of annual budget |
As this table illustrates, compliance costs increase significantly with bank size. While smaller banks allocate a smaller percentage of their budget to compliance, the absolute dollar amount spent by larger banks is considerably higher. This difference highlights the economies of scale enjoyed by larger institutions in managing their compliance programs.
Strategic Resource Allocation for Compliance
Financial institutions are constantly evaluating how to effectively allocate resources for compliance. This involves tough decisions about where to invest and where to cut costs. Some institutions choose to prioritize technology investments, believing that automation will result in long-term cost savings and increased efficiency. Others focus on building internal expertise, recognizing the value of dedicated compliance professionals who understand the intricacies of regulatory requirements.
Building a Compliance Framework That Actually Works

Effective banking regulatory compliance involves more than simply understanding the rules. It requires a practical and adaptable framework integrated into the core of an institution's operations. This means moving beyond simple checklists and building a system that both supports daily activities and ensures adherence to all regulations.
From Theory to Practice: Key Components of a Robust Framework
A strong compliance framework isn't just about avoiding penalties. It's about building a resilient and trustworthy institution. This begins with clear accountability at every level. Every employee, from tellers to executives, needs to understand their individual role in maintaining compliance.
Effective monitoring systems are also essential. These systems should proactively identify potential issues before they become serious regulatory problems. Think of it as a financial early warning system, flagging concerns before they escalate.
Clear and comprehensive documentation is also vital. Well-maintained records are crucial for demonstrating compliance to regulators. This requires efficient and effective documentation processes.
The following table outlines the key elements of a robust banking compliance framework. It details the purpose of each component, the challenges in implementation, and best practices to ensure success.
Key Components of a Robust Banking Compliance Framework: Essential elements that form the foundation of an effective compliance program
| Component | Purpose | Implementation Challenges | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clear Accountability | Defines roles and responsibilities for compliance at all levels. | Ensuring all staff understand their compliance obligations. | Implement regular training and communication programs. |
| Effective Monitoring | Proactive identification of potential compliance breaches. | Integrating monitoring systems with existing workflows. | Leverage technology for automated monitoring and alerts. |
| Comprehensive Documentation | Provides evidence of compliance activities and decisions. | Balancing thorough record-keeping with efficiency. | Implement document management systems and standardized procedures. |
This table provides a clear overview of the building blocks for a successful compliance program. By addressing these key components, institutions can create a solid foundation for regulatory compliance.
Embedding Compliance into Organizational DNA
Leading banks don't treat compliance as a separate department. They integrate it into their core operations, creating a culture where compliance is everyone's responsibility. This ensures that regulatory considerations are a part of every decision, from product development to customer interactions.
For instance, if a bank is developing a new lending product, integrating compliance from the start can avoid costly revisions later. This integrated approach not only minimizes risk but also streamlines operations.
One common challenge is transitioning from a reactive to a proactive compliance approach. This requires a commitment from leadership and a willingness to invest in the right resources. However, the benefits of a well-integrated framework far outweigh the challenges. Learn more about a proven approach to regulatory compliance. A recent survey by the Bank Policy Institute (BPI) highlighted the growing demands compliance places on bank resources. Between 2016 and 2023, employee hours dedicated to regulatory compliance increased by 61%, while overall employee hours only rose by 20%. This emphasizes the need for efficient and effective compliance frameworks.
Building a successful framework requires a commitment to continuous improvement. This involves regularly reviewing and updating policies and procedures and staying informed about evolving regulatory requirements. Ultimately, a robust framework is an investment in the long-term health and stability of any banking institution.
Technology Solutions That Transform Compliance Reality

Technology offers a powerful set of tools for navigating the complexities of banking regulatory compliance. However, not every solution provides the same value. Beyond the marketing hype, which technologies truly offer a worthwhile return on investment? This section explores the practical uses of technologies that are reshaping how banks manage regulatory requirements.
AI-Powered Monitoring: Enhancing Compliance Accuracy
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are changing compliance monitoring. These tools can analyze large datasets, identifying suspicious activity and patterns that human reviewers might miss. This improves both accuracy and efficiency, allowing compliance teams to focus on more strategic work.
For instance, AI-powered systems can flag potentially fraudulent transactions immediately, minimizing financial losses and regulatory exposure. They can also analyze customer data for indicators of money laundering or other illegal activities, ensuring compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations. This allows compliance teams to focus their resources on investigating higher-risk situations.
Blockchain: Building Trust and Transparency
Blockchain technology, initially associated with cryptocurrencies, is also changing compliance. Its inherent immutability and transparency provide powerful capabilities for creating secure audit trails. This can streamline compliance reporting and satisfy even the strictest regulatory examiners.
Consider a loan application process tracked on a blockchain. Every step, from the initial application to the final approval, is recorded and easily verifiable, creating a transparent and tamper-proof record. This significantly reduces the risk of fraud and simplifies audits.
Automation: Streamlining Compliance Workflows
Automation plays a crucial role in simplifying complex compliance workflows. By automating repetitive tasks like data entry and report generation, banks can reduce manual errors and free up staff for more strategic work. This results in substantial cost savings and a more effective use of resources.
Moreover, automation can standardize processes, ensuring consistency across different departments and locations. This lowers the risk of inconsistencies that could attract regulatory scrutiny. You might be interested in: How to master banking data analytics. This approach to leveraging data analytics can help banks better understand and manage their risks, playing a vital role in effective banking regulatory compliance.
Navigating Technology Investment Decisions
Choosing which technology to invest in can be difficult. Banks need to carefully evaluate build-versus-buy decisions and realistically assess integration challenges with existing systems. Practical strategies involve thorough due diligence, pilot programs, and clear metrics for measuring success. A recent survey by the Bank Policy Institute (BPI) found that between 2016 and 2023, employee hours devoted to regulatory compliance increased by 61%, while overall employee hours only increased by 20%. This highlights the need for technology solutions that improve efficiency.
By strategically adopting these technologies, banks can shift their compliance function from a cost center to a source of competitive advantage. This change requires a commitment to innovation and a willingness to embrace the power of technology to improve compliance effectiveness.
Risk Management Strategies That Protect Your Institution
Managing risk in banking is crucial for safeguarding an institution's future. It's not merely about regulatory compliance; it's about building a resilient and secure foundation. This requires moving beyond theoretical models and embracing actionable risk management strategies. Successful banks proactively identify, assess, and mitigate the compliance risks that pose the most significant threats.
Identifying and Assessing Compliance Risks
Leading banks employ comprehensive assessment methodologies to uncover both apparent and hidden risks across all regulatory areas. These methodologies often incorporate detailed internal audits, external reviews, and ongoing monitoring of regulatory changes. This ensures a holistic view of the risk landscape.
For example, a bank might create a risk assessment matrix that analyzes the likelihood and potential impact of various compliance breaches. This allows the institution to prioritize areas posing the greatest threat. This isn't a one-time activity; it's a continuous process adapting to the evolving regulatory environment. Furthermore, successful institutions actively involve front-line staff in risk identification, leveraging their direct experience and insights.
Prioritizing Compliance Efforts Based on Risk Exposure
Effective resource allocation requires prioritizing compliance efforts based on actual risk exposure, not just perceived threats. This focused approach ensures that resources are directed where they can have the most impact.
Consider a bank operating internationally. Different jurisdictions may have varying regulations and penalties. Prioritizing high-risk areas, like those with stricter rules or higher penalties, optimizes resource allocation and maximizes the effectiveness of compliance programs. This targeted approach minimizes wasted effort and strengthens overall compliance. Technology can play a significant role in optimizing these efforts; for more information, explore how to streamline operations and enhance efficiency.
Designing Effective Controls and Early Warning Systems
After identifying and prioritizing risks, designing effective controls is essential. These controls should meet regulatory requirements while minimizing disruptions to daily operations. Leading banks achieve this by integrating compliance directly into their workflows.
This often involves building automated checks and balances into existing systems and processes. For example, a bank might implement automated transaction monitoring systems to detect suspicious activity in real-time. However, controls alone are not sufficient. Early warning systems are crucial for identifying potential issues before they escalate into regulatory problems.
These systems can include regular reporting, internal audits, and even whistleblowing mechanisms. The objective is early detection, enabling timely corrective action. Another valuable resource is How to master stress testing for banks, which explores the vital role of stress testing in risk management.
By implementing robust risk management strategies, banks not only protect themselves from regulatory penalties but also cultivate a stronger, more resilient institution. This proactive approach is essential for navigating the complexities of modern banking and regulatory compliance. It fosters long-term stability and builds trust among customers, investors, and regulators.
The Future of Banking Regulatory Compliance: Be Prepared
The regulatory landscape for banking is in constant flux, and the pace of change is only increasing. Emerging trends are reshaping compliance requirements, meaning institutions must adapt quickly or risk falling behind. Let's explore the key forces driving this change and offer practical guidance on preparing for the future of banking regulatory compliance.
Digital Transformation and Its Regulatory Implications
The increasing digitization of financial services presents both opportunities and challenges. While digital transformation promises greater efficiency and broader reach, it also introduces new risks related to cybersecurity, data privacy, and fraud.
For example, the rise of open banking, where customers share their financial data with third-party providers, requires robust data protection measures and compliance with evolving privacy regulations. The growing use of artificial intelligence and machine learning in financial services also requires careful oversight to ensure fairness, transparency, and accountability. These developments are prompting regulators to prioritize areas like operational resilience and algorithmic auditing, requiring banks to invest in new technologies and expertise.
Changing Customer Expectations and Regulatory Focus
Customer expectations regarding data privacy and financial transparency are also shaping the regulatory agenda. As customers become more aware of how their data is used, regulators are responding with stricter rules and increased enforcement.
This trend is evident in regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). These regulations place greater emphasis on customer consent, data security, and the right to be forgotten, impacting how banks collect, store, and use customer data. Furthermore, growing consumer demand for ethical and sustainable financial practices is leading to increased regulatory focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosures.
Evolving Business Models and Regulatory Adaptability
The banking industry is experiencing a wave of innovation, with new business models emerging that challenge traditional practices. These new models, often driven by fintech companies, require regulators to adapt existing frameworks and develop new approaches to oversight.
The rise of peer-to-peer lending platforms, for instance, challenges traditional lending models and requires new regulatory frameworks to address risks. Similarly, the increasing use of cryptocurrencies in financial transactions necessitates new regulations to mitigate associated risks.
Preparing for the Future of Compliance
Adapting to this evolving regulatory landscape requires banks to take proactive steps:
Embrace a Culture of Compliance: Integrate compliance into the core of the organization, not just as a separate function. This requires training and education programs so all employees understand their compliance responsibilities.
Invest in Technology: Utilize advanced technologies like AI-powered monitoring tools and blockchain for enhanced compliance monitoring and audit trails. This will improve efficiency and effectiveness in managing requirements.
Monitor Regulatory Developments: Stay informed about emerging trends and anticipate future regulatory changes. This proactive approach will allow institutions to adapt quickly and avoid potential penalties.
Collaborate with Regulators: Engage in constructive dialogue with regulators and participate in industry consultations. This open communication will help shape future regulations and ensure compliance efforts are aligned with regulatory expectations.
By proactively addressing these evolving trends, banks can transform regulatory compliance from a cost center into a source of competitive advantage. This requires a commitment to continuous improvement, a willingness to embrace new technologies, and a proactive approach to understanding and anticipating future regulatory changes.
Ready to unlock the power of data-driven decision-making for banking regulatory compliance? Explore Visbanking today and discover how our Bank Intelligence and Action System (BIAS) can help you navigate the evolving regulatory landscape and empower your institution for future success.