Strategic Planning for Banks: Drive Growth & Innovation
Brian's Banking Blog
The Evolution of Strategic Planning for Banks
The financial world is constantly changing, and strategic planning for banks has undergone a significant transformation. Simply opening new branches and hoping for success is a relic of the past. Strategic planning now demands adaptable, multi-faceted frameworks to navigate unpredictable market dynamics. Several key factors have fueled this evolution.
Key Drivers of Change
Technological Disruption: The rise of online banking, mobile payments, and other financial technologies has fundamentally reshaped how customers interact with banks. This necessitates a strategic response, integrating digital channels and innovative services.
Shifting Customer Expectations: Today's customers demand personalized, seamless experiences across all channels. Banks must anticipate and fulfill these evolving expectations to retain existing customers and attract new ones. This means prioritizing the customer experience in strategic planning.
Regulatory Pressures: The regulatory environment for banks is in constant flux, with new compliance requirements and reporting obligations frequently emerging. Strategic plans must incorporate these changes to mitigate risks and ensure compliance. For instance, adapting to open banking regulations requires banks to share customer data securely with third-party providers, impacting their strategic approach to data management and partnerships.
Fintech Competition: The rise of Fintech companies offering specialized financial services has intensified competition within the banking industry. Banks must differentiate themselves by providing unique value and strategically leveraging their existing infrastructure while innovating.
These factors compel banks to abandon rigid annual planning cycles and adopt more agile and responsive approaches, enabling them to adapt to market shifts quickly and effectively. Moreover, strategic progress monitoring is becoming crucial. Recent benchmarks from 2025 reveal that the median central bank employs over 600 staff members, with 50% utilizing progress monitoring tools. Interestingly, only 25% benchmark their success against external metrics, while most rely on key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess operational performance and regulatory compliance. Learn more about these trends here.
From Reactive to Proactive
Traditional strategic planning often centered on reacting to past performance and current market conditions. However, modern strategic planning demands a proactive approach. This involves anticipating future trends, identifying potential disruptions, and developing strategies to seize opportunities or mitigate risks.
Embracing Agility
Modern strategic planning must be agile and adaptable. The era of static five-year plans is over. Banks need to adjust their strategies rapidly in response to market changes. This requires a flexible planning process with regular reviews and revisions. Furthermore, banks are increasingly integrating scenario planning into their strategic frameworks, anticipating various potential market disruptions and developing contingency plans to maintain resilience. Think of it like navigating a ship: a rigid plan is like setting a course and hoping for smooth sailing, while an agile approach allows for course correction based on changing conditions and unexpected obstacles.
This shift towards agility and proactivity empowers banks not only to survive but to thrive in today’s dynamic financial landscape. By embracing change and anticipating future trends, banks can position themselves for long-term success.
Essential Elements of Winning Bank Strategies

Strategic planning for banks isn't a yearly event anymore. It's an ongoing process that demands both adaptability and the ability to anticipate what's next. This means going beyond simple mission statements. It means focusing on the core components that truly set successful banks apart. These elements are the foundation of a strong and flexible strategy.
Crafting a Vision That Guides Decisions
A strong vision statement paints a clear picture of the bank's ideal future. This isn't just a motivational phrase; it's a guiding principle for decisions at every level. For example, a vision centered on leading through technology will naturally lead to investments in innovation and digital upgrades. This focused direction ensures every decision, from product development to marketing, aligns with the overarching strategic goals.
Conducting a Banking-Specific SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) is crucial for understanding a bank's internal capabilities and its external environment. But a generic SWOT analysis isn’t enough. Banks must tailor this process to the specific challenges and opportunities within the financial sector. The expert tips in Strategic Planning Made Simple can offer valuable insights into how strategic planning has changed. This requires a deep look at factors like regulatory changes, new technologies, and competitive pressures. This type of focused analysis provides actionable insights for developing targeted strategies. Learn more about effectively incorporating SWOT analysis with our guide on banking strategic planning.
Establishing Measurable Objectives and Accountability
Clearly defined objectives turn the bank's vision into concrete, measurable targets. These objectives need to be SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Having clear lines of accountability is also essential. This ensures specific individuals or teams are responsible for achieving particular outcomes. This approach creates a sense of ownership and drives progress toward strategic goals.
Developing a Risk Assessment Framework
The banking world is full of risks. Successful banks create robust frameworks to identify, assess, and reduce these risks proactively. This includes looking at things like credit risk, operational risk, market risk, and cybersecurity threats. For instance, a bank might create contingency plans for economic downturns or invest in advanced security to protect against cyberattacks. This kind of proactive risk management protects the bank's stability and its long-term success.
Creating an Actionable Implementation Plan
A strategic plan is worthless without proper execution. This is why a detailed implementation plan is so important. It breaks down the overall strategy into smaller, more manageable steps, outlining timelines, resource allocation, and key milestones. It also sets up clear communication channels to keep everyone informed and working together. This structured approach turns the strategy from a high-level document into a practical roadmap.
The following table outlines key components for a comprehensive bank strategic plan.
Essential Components of Bank Strategic Plans
| Component | Purpose | Implementation Considerations | Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vision Statement | Define the bank's long-term aspirations | Engage stakeholders, ensure alignment with core values | Market share growth, brand recognition, employee satisfaction |
| SWOT Analysis | Identify internal strengths and weaknesses, external opportunities and threats | Conduct thorough research, involve diverse perspectives | Identification of key competitive advantages, development of mitigation strategies |
| Measurable Objectives | Translate vision into concrete targets | Use SMART criteria, align with overall strategic goals | Achievement of specific targets within defined timelines |
| Risk Assessment Framework | Identify and mitigate potential risks | Consider various risk categories (credit, market, operational, cybersecurity), develop contingency plans | Reduced financial losses, improved regulatory compliance |
| Implementation Plan | Outline specific steps and timelines for executing the strategy | Assign responsibilities, allocate resources, establish communication channels | Completion of milestones, achievement of strategic objectives |
This table summarizes the crucial elements of a bank's strategic plan. It highlights how each part contributes to the overall success of the plan.
A well-defined implementation plan helps ensure the strategic vision becomes a reality. This leads to tangible results, impacting everything from better customer satisfaction to increased profits and a stronger competitive position. These core elements work together to create a robust strategic base, enabling banks not just to survive, but to thrive in a constantly evolving environment.
Technology Investment as Your Competitive Advantage

Technology has taken center stage in the banking industry. It's the backbone of modern banking operations and a key driver of future success. This shift requires banks to prioritize strategic technology investments that foster growth and create a competitive edge.
Balancing Run-The-Business and Transformation
Leading banks recognize the importance of balancing the maintenance of existing technology ("run-the-business") with investments in innovative solutions ("change-the-business"). Keeping core systems running smoothly is essential, but real competitive advantages arise from using technology to transform operations and customer experiences. This means strategically allocating resources to initiatives that boost efficiency, improve customer engagement, and generate new revenue.
For example, a bank might invest in upgrading its core banking system to improve transaction processing speeds and reduce costs (run-the-business). At the same time, it might invest in developing a personalized mobile banking app with customized financial advice and integrated budgeting tools (change-the-business). This balanced approach ensures the bank remains competitive and builds a foundation for future growth.
Frameworks For Technology Investment Decisions
Effective technology investments require more than simple ROI calculations. They need a broader strategic framework that considers customer impact, competitive positioning, and long-term adaptability. This involves a deep understanding of market trends and a clear vision for the bank's future.
Successful institutions also develop clear evaluation criteria for technology priorities, ensuring alignment with overall strategic goals. For example, investing in AI-powered fraud detection software might be prioritized if enhancing security and minimizing losses is a key objective.
Partner Selection and Implementation
Choosing the right technology partners is crucial. Banks need partners who offer leading-edge solutions and understand the specific needs of the financial industry. Effective implementation is equally important. Many digital initiatives fail due to poor project management, inadequate training, and a lack of stakeholder buy-in. A strategic approach to implementation with realistic timelines and clear roles is essential.
Strategic planning must include comprehensive partner selection and implementation strategies. Global banks are expected to invest US$176 billion in IT by 2025, up from US$147 billion in 2022. This investment is vital for digital transformation, yet only 39% of this spending is allocated to change-the-business initiatives. More detailed statistics can be found here.
Measuring Technology Success
Measuring the success of technology investments requires focusing on key metrics. While cost reduction is important, true value lies in improved customer retention, increased operational efficiency, and new revenue generation. These metrics reflect the actual impact of technology on a bank’s bottom line and long-term success.
By taking a strategic approach to technology investment, banks can position themselves for growth, strengthen their competitive advantage, and deliver greater value to their customers.
Integrating AI Into Your Banking Strategy
Artificial intelligence is no longer a futuristic concept for banks. It's quickly becoming a key part of strategic planning. But how are successful banks moving past the experimental stage and truly integrating AI for a competitive edge? The key is shifting from focusing on AI's novelty to strategically applying it where it delivers measurable results.
From Pilot Projects to Core Operations
Many banks have experimented with AI through pilot projects. Moving from these experiments to system-wide integration, however, requires a strategic approach. This involves identifying core operational areas where AI can have the biggest impact. Think fraud detection, customer service, and risk management. For instance, AI-powered chatbots can handle routine customer questions, freeing up human agents for more complex issues. This improves efficiency and enhances the customer experience. Want to learn more about predictive analytics in banking? Check out this helpful resource: How to master predictive analytics in banking.
Prioritizing AI Use Cases for Strategic Impact
Not all AI applications are the same. Strategic planning should prioritize AI use cases based on their potential to improve key performance indicators (KPIs) and contribute to overall business goals. This means focusing on areas where AI delivers tangible results, not just following the latest trends. Consider using AI for personalized financial advice to strengthen customer relationships and drive revenue growth. This targeted approach maximizes the return on AI investments. The banking sector's approach to AI investment is a significant shift in strategic planning. The global AI market is expected to surpass $1 trillion by 2030. While banks heavily experimented with AI in 2024, getting accurate results was often more complex and costly than expected. As a result, 2025 is predicted to be a year of more strategic focus, with banks prioritizing use cases based on specific KPIs. Learn more about these trends: Banking Predictions and Theme Analysis.
Building the Right Organizational Structure
Successfully integrating AI takes more than just technology; it requires the right organizational structure. This means establishing dedicated AI teams with the necessary expertise and creating clear lines of responsibility. Collaboration between IT, business units, and data science teams is also essential. This breaks down silos and ensures alignment between AI projects and the overall business strategy. This integrated approach allows banks to effectively implement and manage AI solutions.
Addressing the Challenges of AI Adoption
Integrating AI into banking has its challenges, from ensuring data quality to navigating regulatory hurdles. Data quality is crucial for accurate AI insights. Banks often struggle with fragmented data sources and inconsistencies. Addressing these issues through data cleansing and consolidation is vital for effective AI implementation. Clean data isn't enough; complying with data privacy regulations is also essential.
Overcoming Obstacles to Create Competitive Advantage
Despite these challenges, many banks are successfully integrating AI to gain real competitive advantages. They're doing this by focusing on data quality, investing in strong AI infrastructure, and developing effective change management strategies. This helps them personalize customer experiences, automate processes, and improve risk management. Another key factor is building internal AI expertise, empowering banks to develop custom AI solutions for their specific needs. By tackling these challenges head-on and focusing on strategic implementation, banks can unlock the full potential of AI and position themselves for success in the changing financial landscape.
Building Customer-Centric Banking Strategies

In the banking industry, technology and innovation are important, but they're useless if they don't serve the customer. Strategic planning for banks must prioritize a customer-centric approach, moving away from product-focused strategies. This change is crucial for sustainable growth in the modern financial world.
Understanding the Customer-Centric Shift
Moving to a customer-centric model means understanding customer needs and tailoring services accordingly. This requires shifting from pushing products to anticipating customer desires and building solutions around them. This customer-focused approach builds loyalty and drives long-term success.
For example, instead of just selling accounts, a customer-centric bank analyzes customer spending to offer personalized budgeting tools and financial advice. This proactive approach helps customers manage their finances more effectively.
Gathering Actionable Customer Insights
Understanding customers requires effective methods for gathering actionable insights. Journey mapping helps visualize the customer experience, identifying pain points and improvement opportunities.
Data analytics reveals customer behavior, providing insights into product preferences and channel usage. Voice-of-customer programs, like surveys and feedback forms, offer direct customer input for strategic decisions.
Integrating AI into banking strategies is increasingly important; you can explore applications of AI in customer support. This technology can deepen customer understanding and improve service.
Translating Insights into Strategic Decisions
Gathering insights is only the first step. Banks must translate these insights into strategic decisions about product development, channel optimization, and service delivery.
This could involve developing new products based on identified needs, improving digital channels based on usage patterns, or implementing new service protocols based on feedback. These data-driven decisions ensure offerings resonate with customers. Strategic planning should also consider how technology can automate processes and improve customer interactions.
Notably, 87.2% of central banks have digital transformation and payment systems among their top strategic goals for 2025. These institutions have lean strategic planning units, averaging just under five staff members, and 33% link staff pay to strategic plan objectives. Explore this topic further here.
Meaningful Customer Segmentation
Effective customer segmentation goes beyond demographics. It involves grouping customers based on needs, behaviors, and value. This allows for targeted value propositions for each segment.
For example, a bank might segment customers based on financial goals (retirement, buying a home) and develop tailored products and services. This targeted approach improves engagement and drives profitability.
Developing Targeted Value Propositions
Defining segments is followed by developing compelling value propositions. This means crafting a clear message communicating the unique benefits of offerings to each segment.
This might involve highlighting product features, emphasizing customer service, or showcasing the bank's commitment to social responsibility. A strong value proposition resonates with the target audience and drives acquisition and retention.
By adopting a customer-centric approach to strategic planning, banks can build stronger relationships, enhance customer loyalty, and drive sustainable growth. This focus ensures technology and innovation empower customers and build a thriving future for the bank.
Measuring What Matters: KPIs That Drive Results
Strategic planning for banks depends heavily on choosing the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). These metrics offer a measurable method for tracking progress, pinpointing areas for improvement, and gauging the success of strategic initiatives. High-performing institutions recognize that tracking traditional financial metrics alone is no longer sufficient.
Moving Beyond Traditional Metrics
Metrics like Return on Assets (ROA) and Net Interest Margin (NIM) are still important, but effective strategic planning requires a more comprehensive approach. Modern banks are using balanced scorecards which include a wider array of KPIs. These include customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and innovation momentum. This broader view ensures strategic planning focuses on long-term success, not just financial gains.
For example, a bank might gauge customer satisfaction through surveys and online reviews, tracking metrics like Net Promoter Score (NPS) and customer retention rates. This offers valuable insights into customer service effectiveness and highlights areas for improvement.
You might be interested in: How to master bank financial planning.
Establishing Meaningful KPIs
The best KPIs align directly with your strategic objectives. They should offer clear, actionable insights that inform decision-making. They also serve as early warning signs when things go off track. This link between KPIs and strategic goals ensures that every metric contributes to the plan's overall success. It also avoids the trap of tracking vanity metrics that appear impressive but don't drive meaningful results.
From Vanity Metrics to Actionable Indicators
The difference between a vanity metric and an actionable indicator lies in the ability to influence the outcome. Website visits could be a vanity metric. However, the conversion rate of those visits into new account openings is an actionable indicator. Focusing on actionable indicators empowers banks to make data-driven decisions that directly impact performance.
Dashboards That Drive Decision-Making
KPIs are most effective when presented clearly and concisely. Well-designed dashboards consolidate key metrics into a single view. This provides a real-time snapshot of performance. Visualizing data simplifies analysis and leads to faster, more informed decision-making.
The following infographic illustrates the distribution of bank risk exposure across different categories:
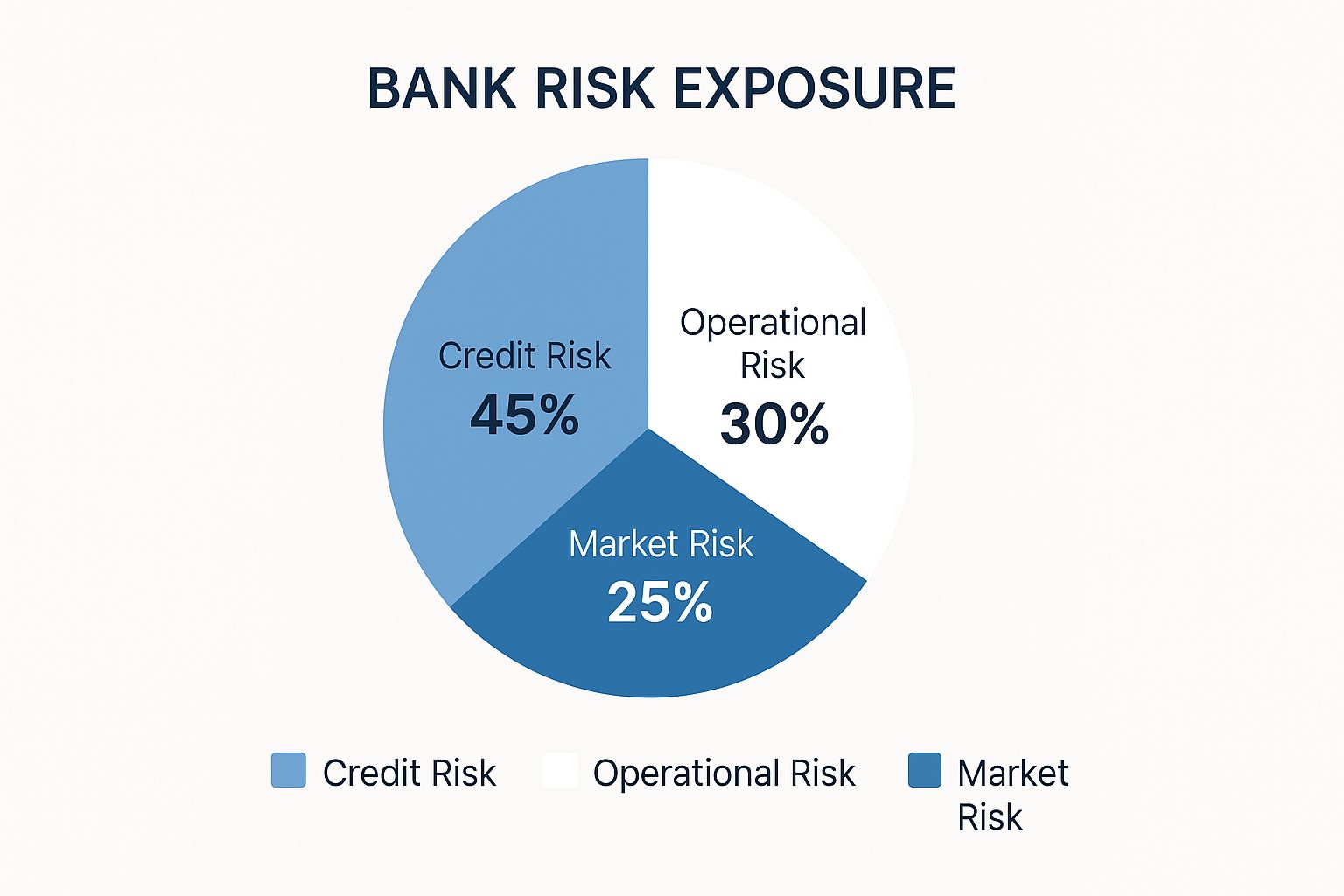
As the infographic shows, credit risk (45%) poses the largest risk exposure for banks. This is followed by operational risk (30%) and market risk (25%). This visualization emphasizes the need for balanced risk management, strategically addressing each category.
Implementing Effective Performance Review Cycles
Regular performance reviews are crucial for maintaining accountability and adapting to changing market conditions. These reviews should assess progress toward strategic objectives, identify roadblocks, and allow for necessary plan adjustments. This iterative approach keeps strategic planning dynamic and responsive to the evolving financial landscape.
The following table categorizes key performance indicators (KPIs) that banks should consider incorporating into their strategic planning and performance measurement frameworks.
Strategic Banking KPIs: Categories and Examples
| KPI Category | Example Metrics | Strategic Relevance | Measurement Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Performance | ROA, NIM, Efficiency Ratio | Profitability and financial stability | Quarterly/Annually |
| Customer Satisfaction | NPS, Customer Retention Rate, Customer Churn Rate | Customer loyalty and growth | Monthly/Quarterly |
| Operational Efficiency | Cost per Transaction, Transaction Processing Time, Automation Rate | Operational effectiveness and cost reduction | Monthly/Quarterly |
| Innovation | Number of New Products Launched, Adoption Rate of New Technologies | Future growth and competitive advantage | Quarterly/Annually |
| Risk Management | Loan Loss Provision, Number of Fraud Incidents, Regulatory Compliance Rate | Risk mitigation and financial stability | Monthly/Quarterly |
This table offers examples of KPIs across different categories. By carefully selecting and tracking the right metrics, banks can gain valuable insights into their performance, make informed decisions, and achieve their strategic goals.
Ready to empower your bank with data-driven insights and elevate your strategic planning? Visit Visbanking today to learn more about how our Bank Intelligence and Action System (BIAS) can transform your decision-making process.