Managing Interest Rate Risk: Proven Strategies for Success
Brian's Banking Blog
The Real Impact of Interest Rate Risk in Today's Market

Interest rate risk isn't just a number on a financial statement; it's a major factor affecting an institution's overall financial well-being. Changes in interest rates can significantly impact profits and even long-term stability. Think of it like sailing a ship: calm waters (stable rates) make for smooth sailing, but unexpected storms (volatile rates) can quickly throw a ship off course. This is why understanding and managing interest rate risk is so important.
Different Types of Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk comes in different forms, each requiring a specific management approach. Repricing risk, for example, comes from the difference in timing between when assets and liabilities reprice. A bank using short-term deposits to fund long-term loans faces higher repricing risk if interest rates increase. Their cost of funds grows faster than income from loans, shrinking profit margins.
Yield curve risk refers to the impact of changes in the shape of the yield curve. Imagine the yield curve as a predictor of future interest rates. A flattening curve may signal an economic slowdown and potential losses on long-term investments.
Basis risk happens when interest rates on different instruments don't move together. This makes hedging strategies more complex because one instrument might not fully offset the risk of another. Finally, features like optionality in financial instruments, such as callable bonds, add another layer of complexity. These options give one party the right, but not the requirement, to take a certain action, creating uncertainty about future cash flows.
Regulatory Oversight and Interest Rate Risk
Managing interest rate risk is crucial for financial institutions, especially banks overseen by regulators like the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC). The OCC conducts regular reviews to assess the interest rate risk of midsize and community banks, as well as federal savings associations. These reviews are vital because they help banks prepare for potential interest rate fluctuations, which can significantly impact their financial health.
For example, when interest rates rise, banks might see less demand for loans and higher costs for deposits, impacting their profitability. The OCC's Interest Rate Risk Statistics Reports offer valuable insights into these risks, helping banks develop effective risk management strategies. This proactive approach helps maintain financial stability in the banking sector, ensuring banks can continue lending securely and efficiently.
The size and complexity of a financial institution also influence how interest rate risk is experienced and managed. Larger institutions often have more resources and sophisticated tools for analyzing and mitigating risk. However, their interconnectedness within the financial system can create systemic risks impacting the entire market. Smaller institutions, while less complex, may have fewer resources and face unique challenges in adapting to rapid rate changes. Recent interest rate volatility has highlighted the need for flexible strategies that can adapt to a constantly changing financial environment.
Battle-Tested Strategies for Managing Interest Rate Risk
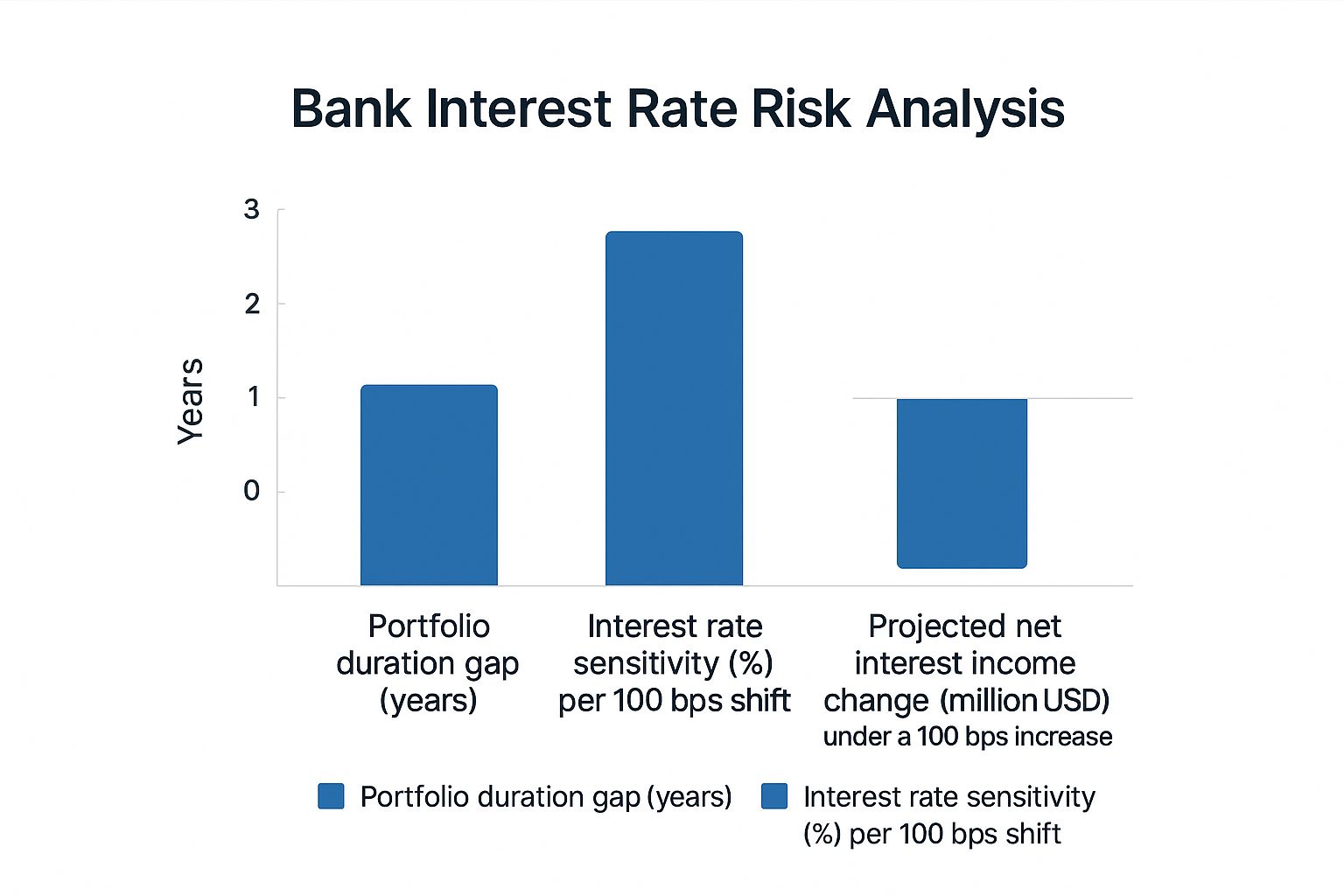
The infographic above illustrates key data points for managing interest rate risk. These include the portfolio duration gap, interest rate sensitivity, and the projected change in net interest income under a 100 basis point interest rate increase. Even a small shift in rates can significantly impact an institution's profitability. This underscores the need for a robust risk management strategy.
Traditional and Modern Approaches
Managing interest rate risk effectively requires a combination of proven methods and newer techniques. Duration matching, a classic approach, aims to align the duration of assets and liabilities. This minimizes the effect of interest rate changes on the net present value of the portfolio.
Gap analysis assesses the difference between rate-sensitive assets and liabilities within specific timeframes. This helps pinpoint potential vulnerabilities to rate shifts. However, these traditional methods alone may not be sufficient in today’s volatile market.
Consider the rapid market shifts during the COVID-19 pandemic. Traditional models often struggled to accurately predict the impact of these unprecedented changes. This highlights the need for more dynamic and responsive risk management strategies.
Leveraging Derivatives and Structured Products
Financial institutions are increasingly using derivatives and structured products in their risk management strategies. Interest rate swaps, for example, allow institutions to exchange fixed and floating interest rate payments. This effectively transforms the nature of their interest rate exposure.
Futures contracts offer standardized agreements to buy or sell a financial instrument at a predetermined price and date. They provide a valuable tool to hedge against future rate movements. Options give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell at a specified price. This offers more flexibility in managing risk.
These advanced techniques offer greater precision and flexibility. However, they also require specialized expertise for effective implementation. Check out our guide on How to master interest rate risk.
Risk Appetite and Strategy Alignment
The best strategy for managing interest rate risk depends on an institution's specific risk appetite. A more risk-averse institution might prefer conservative hedging strategies, prioritizing capital preservation.
An institution with a higher risk tolerance may employ more dynamic strategies. This means accepting some level of volatility to pursue higher returns. The broader economic context, including regulatory factors and market trends, also plays a vital role. You might be interested in: impact of speed on your bottom line.
The Federal Reserve (Federal Reserve) considers interest rate risk management a key focus. The Fed’s balance sheet is affected by interest rate fluctuations due to its large holdings of Treasury securities. During periods of rising Treasury yields, the value of these securities can decrease. For example, in 2018 and during the COVID-19 pandemic, the Fed responded by lowering interest rates and purchasing Treasury securities.
The following table summarizes several interest rate risk management strategies. It compares their effectiveness, complexity, cost, and suitability for different types of financial institutions.
Interest Rate Risk Management Strategies Comparison
| Strategy | Effectiveness | Implementation Complexity | Cost | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duration Matching | High | Moderate | Moderate | Banks, Pension Funds |
| Gap Analysis | Moderate | Low | Low | Banks, Credit Unions |
| Interest Rate Swaps | High | High | High | Large Banks, Corporations |
| Futures Contracts | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Banks, Hedge Funds |
| Options | Moderate | High | Moderate | Banks, Investment Firms |
This table highlights the trade-offs between complexity, cost, and effectiveness for each strategy. Choosing the right strategy requires carefully balancing these factors. It also requires a thorough understanding of the institution's overall financial objectives.
Using Historical Data to Predict Future Rate Movements

Managing interest rate risk isn't just about reacting to the current market. It's about understanding the past to anticipate the future. This means digging into historical interest rate patterns to gain valuable insights for future rate movements. Smart institutions are using historical data not just as a record, but as a powerful predictive tool.
Learning From the Past Without Repeating It
Historical data offers a wealth of information on how interest rates have behaved in different economic climates. But it's important to avoid the trap of thinking "this time is different." While every market cycle has its unique characteristics, historical patterns can still teach us valuable lessons.
For example, looking at past periods of rising inflation can illuminate how interest rates reacted and the impact on various sectors. This knowledge can better prepare us for future inflationary periods.
Analyzing the lead-up to past recessions can also help pinpoint potential warning signs to guide investment decisions. By studying asset class performance during previous downturns, we can gain insights into their potential future behavior. Historical data on interest rates provides crucial insights for managing interest rate risk. The U.S. Department of the Treasury, for example, offers historical data on interest rates going back to 2000.
This data is key for analyzing interest rate trends and patterns over time. For instance, the average U.S. Fed Funds interest rate has been around 5.41% from 1971 to recent times. Understanding these historical trends helps financial institutions and policymakers predict future interest rate movements and adjust their strategies. Projections indicate the U.S. Fed Funds rate is expected to trend downwards to around 3.50% by 2026, according to econometric models. Find more detailed statistics here.
To better illustrate historical trends and their effects, let's examine the following table:
Historical Interest Rate Trends and Their Impact
This table presents key historical interest rate periods, the factors that drove rate changes, and the resulting effects on different financial instruments and institutions.
| Time Period | Interest Rate Movement | Key Drivers | Impact on Banks | Impact on Borrowers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1970s | High and Volatile | Oil crisis, inflation | Increased profitability from higher lending rates, but also higher risk of loan defaults | Higher borrowing costs, reduced access to credit |
| 1980s | Declining | Federal Reserve policy to combat inflation | Decreased profitability from lower lending rates, increased competition | Lower borrowing costs, increased access to credit |
| 2008-2009 | Near Zero | Financial crisis, recession | Reduced profitability, increased pressure on net interest margins | Very low borrowing costs, but tighter lending standards |
| 2022-2023 | Increasing | Inflation, Federal Reserve policy tightening | Increased profitability from higher lending rates, but also concerns about potential economic slowdown | Higher borrowing costs, reduced demand for loans |
Key takeaway: Interest rate fluctuations, driven by a combination of economic and policy factors, create both opportunities and challenges for financial institutions and borrowers. Understanding these historical dynamics is essential for navigating the complexities of interest rate risk management.
Stress Testing With Real-World Scenarios
Using historical data also informs stress testing methods. Instead of relying only on theoretical extremes, leading institutions incorporate real-world scenarios based on past market events. This allows for better assessment of vulnerability to various shocks and more informed decision-making.
This approach provides a more accurate and nuanced understanding of potential performance in a genuine crisis. This is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate risks and enhance resilience. For more on predictive analytics, see How to master predictive analytics.
Combining Backward-Looking Analysis With Forward Indicators
While historical data is invaluable, it has limitations. It can’t predict the future, especially when unexpected events occur. This is why combining historical analysis with forward indicators is vital for a strong risk management framework.
Forward indicators, like economic forecasts, inflation expectations, and central bank pronouncements, offer insights into potential future interest rate movements. By integrating these indicators with historical analysis, financial institutions get a more comprehensive perspective. This allows them to adjust their strategies to manage interest rate risk effectively in a constantly shifting environment.
Building Your Interest Rate Risk Management Framework
A solid understanding of interest rate risk and potential mitigation strategies is essential. But putting these concepts into a practical framework within your organization is the key to effective risk management. This goes beyond simply creating documents; it's about building a dynamic system that informs decisions and builds resilience.
Establishing Effective Governance
Successful risk management begins with a clear governance structure. This involves defining roles, responsibilities, and lines of authority related to interest rate risk. For instance, a dedicated risk management committee can provide oversight, while assigning specific duties to individuals or teams ensures accountability.
This structure isn't about red tape. It's about establishing a system where decisions are made transparently and efficiently. It ensures everyone understands their role in managing interest rate risk, promoting a proactive risk culture across the organization.
Setting Meaningful Risk Limits
Establishing risk limits is vital for controlling exposure. These limits act as safeguards, defining the acceptable level of risk the institution is willing to assume. These limits shouldn’t restrict growth; they should be flexible, reflecting the institution’s risk appetite and market conditions.
Consider risk limits like the budget for a project. They provide necessary financial guidelines without preventing the team from achieving its objectives. Similarly, well-defined risk limits protect the institution without unduly restricting its operations.
Implementing a Robust Monitoring System
Effective monitoring provides early warnings of potential issues, allowing for prompt intervention. This involves tracking key metrics, such as interest rate sensitivity and portfolio duration. Utilizing tools like Tableau that offer real-time insights into risk exposures is also beneficial. This proactive approach replaces lagging indicators with timely data, allowing for quick adjustments to strategies as needed.
Imagine a doctor monitoring a patient’s vital signs. A heart rate monitor (monitoring) alerts the doctor to potential problems (interest rate risks) before they become critical. This early warning allows for interventions, ensuring the patient’s well-being.
Generating Actionable Reports
Reports shouldn't just document the past; they should guide future action. Reports need to be clear, concise, and tailored to the intended audience. Executive summaries should focus on strategic implications, while operational reports should offer detailed insights for daily decision-making.
This means going beyond simple data summaries and providing actionable insights. For example, a report might not only highlight a potential exposure but also suggest specific hedging strategies or portfolio adjustments. This empowers both management and operational teams to address risks proactively.
Integrating Risk Management Across the Organization
Interest rate risk management isn't a standalone function; it needs to be integrated into the institution's overall risk strategy. This requires collaboration across different departments, including treasury, lending, and investments. A unified approach ensures everyone is working towards a common goal: building a more resilient institution.
This comprehensive approach to risk management strengthens the entire organization. It breaks down barriers, encourages better communication, and creates a culture of shared responsibility. This integrated framework promotes sounder decision-making and ultimately contributes to greater financial stability and long-term success.
Tech Tools Transforming Interest Rate Risk Management

The days of relying solely on spreadsheets and basic models for interest rate risk management are over. Today, financial institutions are adopting advanced technologies to stay competitive. This shift is driven by increasingly complex financial markets and the need for dynamic, real-time risk assessment. But how can you tell which tech solutions offer real value?
AI and Machine Learning: Separating Hype From Reality
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are common terms in finance. But applying them to interest rate risk management requires careful thought. AI can analyze large amounts of data to find patterns and anomalies. However, it's not a perfect solution. The true value of AI is its ability to enhance existing risk models, not replace them.
For example, AI can refine stress testing scenarios. It does this by incorporating non-linear relationships and tail risks that traditional models may miss. Machine learning algorithms can also improve the accuracy of forecasting models. They identify subtle relationships between interest rates and other economic variables. This leads to more reliable predictions of future rate movements, allowing for proactive risk mitigation.
However, the "black box" nature of some AI algorithms can be a problem. It creates challenges for transparency and regulatory compliance. Choosing AI solutions that offer explainable results and integrate with existing risk management frameworks is essential.
Integrated Asset-Liability Management (ALM) Platforms
Integrated ALM platforms are a major step forward in managing interest rate risk. These platforms bring together data from multiple sources, providing a complete view of an institution’s assets and liabilities. This eliminates data silos and speeds up decision-making.
An integrated ALM platform can simulate the impact of different interest rate scenarios on the entire balance sheet. This allows for quick assessment of potential risks and opportunities. Risk managers can then make informed decisions quickly, a critical factor in today's fast-paced markets. These platforms often include sophisticated reporting tools that improve communication and collaboration.
Real-Time Monitoring and Risk Responsiveness
Reacting quickly to interest rate changes is essential in today’s volatile markets. Real-time monitoring tools allow institutions to constantly track key risk metrics. This provides immediate alerts to potential exposures, enabling timely interventions.
Real-time dashboards can display key indicators. These might include duration gaps and net interest income sensitivity. This gives risk managers up-to-the-minute insights into their risk profile. This real-time visibility enhances risk responsiveness, letting institutions adjust their hedging strategies and portfolio allocations dynamically.
Evaluating ROI and Avoiding Overengineering
Investing in new technology requires careful evaluation of the return on investment (ROI). While advanced tools can offer significant benefits, it's important to avoid overspending on overly complex solutions. The right technology should align with the institution's size, complexity, and specific risk management needs.
Successful technology implementation requires thorough planning and execution. Integrating new systems with existing infrastructure can be complex. Institutions should prioritize solutions that integrate easily and minimize disruption to operations. By choosing the right tools and implementing them effectively, institutions can significantly improve their interest rate risk management. This leads to valuable insights, better decision-making, and a more resilient and profitable organization.
Navigating the Regulatory Maze While Managing Risk
Managing interest rate risk isn't just about internal strategies. It's also about understanding the complex world of regulatory compliance. While these regulations might sometimes feel like a burden, they can actually strengthen your overall risk management approach. They provide a solid framework for sound financial practices and build trust with stakeholders.
Decoding Regulatory Requirements
Major authorities like the Basel Committee, the Federal Reserve, and the ECB set strict requirements for managing interest rate risk. Understanding these requirements is essential for avoiding penalties and maintaining a strong reputation. For instance, the Basel Accords outline minimum capital requirements for banks, partially based on their interest rate risk exposure. These regulations ensure banks have enough capital to handle potential losses from interest rate fluctuations.
Turning Regulatory Stress Tests Into Business Insights
Regulatory stress tests are often viewed as a compliance exercise, but they can provide valuable business insights. These tests require institutions to analyze their vulnerability to extreme, yet plausible, economic scenarios. This process can expose hidden weaknesses and inform strategic decisions. By viewing stress tests as a learning opportunity, financial institutions can identify areas for improvement and enhance their risk management framework. Check out our guide on regulatory compliance for banks.
Building Relationships With Regulators
Open communication with regulators is crucial for a proactive approach to regulatory compliance. Building strong relationships with regulatory bodies can create a competitive edge. It opens doors for clarification and feedback, allowing institutions to better understand regulatory expectations and adjust their risk management strategies accordingly. For example, early engagement with regulators when developing new financial products can ensure compliance and prevent costly revisions.
Practical Approaches to Regulatory Compliance
Preparing for regulatory examinations doesn't have to be disruptive. Clear internal procedures and organized records can streamline the examination process. This involves having a well-defined process for collecting and presenting data, along with designated personnel to manage the examination.
Responding effectively to regulatory findings demands quick action and clear communication. Institutions should address findings promptly with detailed remediation plans. Transparency and cooperation are essential for building trust with regulators and showing a commitment to strong risk management. Consider how technological advancements like artificial intelligence can improve your risk management framework. Learn more about Intelligent Process Automation.
Staying Ahead of the Curve
The regulatory landscape is constantly changing. Financial institutions must stay informed about new regulations and emerging trends. This includes monitoring regulatory announcements, attending industry conferences, and participating in regulatory workshops. You might be interested in: How to master regulatory compliance. By being proactive, institutions can adapt to changing requirements and maintain a robust risk management framework, ensuring long-term stability.
The Future of Managing Interest Rate Risk: What's Next
The interest rate risk landscape is constantly shifting, pushing financial institutions to adopt proactive strategies. This means anticipating future hurdles and opportunities, not just reacting to current market conditions. What will shape interest rate risk management in the coming years?
Emerging Challenges and Opportunities
Several key trends are transforming how institutions manage interest rate risk. For instance, Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) could significantly alter interest rate dynamics. Widespread CBDC adoption could influence how central banks control and manage interest rates, impacting the transmission mechanism of monetary policy.
Climate risk is another growing factor. Physical risks, such as extreme weather, can disrupt economic activity and affect interest rates. Transition risks, arising from policy changes and technological advancements aimed at mitigating climate change, can also create interest rate volatility.
Structural changes in financial markets, like the growing role of non-bank financial institutions, also present new exposures. These institutions may operate outside traditional regulatory frameworks, potentially adding new complexities to interest rate risk management.
Building Organizational Resilience
Successfully navigating this changing environment requires building organizational resilience. This involves creating flexible strategies adaptable to various scenarios. Institutions need to go beyond static models, embracing dynamic approaches that reflect the interconnected nature of global markets.
A key aspect of building resilience is fostering a strong risk culture. This involves raising awareness of interest rate risk throughout the organization. It also means clearly defining roles, responsibilities, and communication channels for risk management.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Even with the best planning, institutions can encounter obstacles. One common trap is over-reliance on historical data. While historical data offers valuable insights, it cannot predict the future, especially in volatile markets. Another misstep is focusing only on short-term risks while overlooking longer-term trends. A balanced strategy considers both short-term fluctuations and long-term structural shifts.
Evaluating Your Current Risk Management Effectiveness
To prepare for the future of interest rate risk management, a thorough assessment of your current practices is crucial. Consider the following:
- Model Validation: Are your risk models regularly updated and validated to reflect current market conditions and regulations?
- Scenario Analysis: Do your stress tests incorporate diverse scenarios, including historical events and potential future disruptions?
- Technology Integration: Are you leveraging technology, such as integrated ALM platforms and real-time monitoring tools, to enhance risk management?
- Risk Governance: Is your risk governance structure clear, with well-defined roles, responsibilities, and reporting procedures?
- Regulatory Compliance: Do your risk management practices align with current and anticipated regulatory requirements?
Addressing these areas can strengthen your institution's risk management framework, building resilience and ensuring long-term success in a dynamic financial environment.
Ready to enhance your interest rate risk management and navigate the complexities of finance? Explore Visbanking's Bank Intelligence and Action System (BIAS). Learn more about how Visbanking empowers banks.