Financial Data Quality Management for Business Success
Brian's Banking Blog
Why Financial Data Quality Is Your Competitive Advantage

In the competitive financial world, high-quality data is essential. Think of your financial data as the foundation of your business. A weak foundation creates instability, while a strong one supports growth and stability. Robust financial data quality management ensures the success of your financial institution. This means collecting, storing, and verifying the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of your data.
This allows you to make informed decisions, optimize performance, and maintain a competitive edge.
The High Cost of Poor Data Quality
Poor financial data quality creates a ripple effect of negative consequences. Inaccurate data can lead to faulty financial reporting, damaging your reputation with investors and regulators. Incomplete data hinders your ability to identify trends and make strategic decisions.
Poor data quality can mean lost revenue and missed opportunities. Correcting data errors can be a time-consuming and costly process, diverting resources from strategic initiatives.
A 2024 global survey of over 550 data and analytics professionals highlighted these concerns. 64% of organizations identified data quality as their primary challenge impacting data integrity, directly affecting decision-making. 67% admitted they don't completely trust the data they use for business or financial strategies.
Consequently, data quality was the highest priority for data integrity efforts in 60% of organizations. This shows a widespread concern about the reliability and accuracy of financial data. Find more detailed statistics here: Data Quality Remains Top Data Integrity Challenge
Turning Data Quality into a Strategic Asset
Effective financial data quality management offers a significant competitive advantage. High-quality data empowers you to make better, faster decisions, optimizing resource allocation and improving profitability. This involves implementing robust data governance frameworks, investing in data quality tools, and fostering a culture of data literacy.
Benefits of Effective Financial Data Quality Management
- Improved Decision-Making: Accurate and complete data provides a clear view of your financial health, enabling better decisions.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Streamlined data processes reduce manual effort and errors, freeing up resources.
- Reduced Risk and Improved Compliance: High-quality data helps mitigate financial risks and ensures regulatory compliance.
- Increased Profitability: Reliable data insights lead to more effective strategies for revenue and cost optimization.
By prioritizing financial data quality, you’re investing in the future success of your institution. In the next section, we’ll explore building a robust financial data quality framework.
Building Your Financial Data Quality Framework That Works

A successful financial data quality management framework takes time and effort. It needs a structured approach, combining clear governance, defined metrics, and strong validation. This means going beyond basic compliance checklists and building a system that actively improves your data. Instead of reacting to errors, a strong framework helps prevent them.
Establishing Clear Governance Policies
Effective data governance is the bedrock of managing financial data. These policies outline responsibilities, define data standards, and set procedures for handling data throughout its lifecycle. But governance shouldn't restrict usability. The goal is balance: a system that's both thorough and practical. For a deeper dive, check out this resource: How to master data governance in banking. Clear governance ensures everyone knows their role in maintaining data quality.
Defining Meaningful Quality Metrics
Measuring the effectiveness of your financial data quality management requires the right metrics. These metrics should go beyond simple accuracy and completeness. Consider factors like timeliness, consistency, and relevance to your specific business needs. Identify the data points that truly impact your decisions and focus on improving their quality. This focused approach helps you track progress and identify areas for improvement.
Creating Robust Validation Processes
Validation processes are the guardians of your financial data. They ensure incoming data meets your quality standards. This might involve automated checks, manual reviews, or a combination of both. But effective validation shouldn't create roadblocks. Design processes that catch errors early without slowing down operations. This proactive approach minimizes the impact of bad data on your decisions.
Structuring Data Stewardship Roles
Data stewardship ensures accountability for data quality. This means assigning clear ownership for different data domains and empowering stewards to enforce data governance policies. Avoid unnecessary bureaucracy. Instead, encourage collaboration and communication between data stewards and other stakeholders. This teamwork ensures everyone works together to maintain data quality.
To understand the core building blocks of a robust financial data quality management system, let's explore the following table. It details the essential components and their functions, common implementation challenges, and key success metrics.
| Component | Primary Function | Implementation Challenges | Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Governance | Establishing policies, standards, and procedures for data management | Resistance to change, lack of clear roles and responsibilities, inadequate communication | Policy adherence rate, data quality issue resolution time |
| Data Quality Metrics | Defining and tracking key indicators of data quality | Selecting appropriate metrics, data collection and reporting challenges | Data quality score improvements, reduction in data-related errors |
| Validation Processes | Ensuring data accuracy and completeness before it enters systems | Balancing automation with manual review, maintaining validation rules, integration with existing systems | Error detection rate, reduction in invalid data entries |
| Data Stewardship | Assigning ownership and responsibility for data quality within specific domains | Lack of clear ownership, insufficient training and resources for stewards, difficulty in enforcing policies | Data quality improvements within assigned domains, increased stakeholder engagement |
| Regulatory Compliance & Security | Adhering to relevant regulations and implementing security measures | Keeping up with evolving regulations, balancing security with usability, managing access controls | Compliance audit pass rate, number of security incidents |
This table provides a concise overview of the key elements of a successful data quality management framework. By addressing these components, financial institutions can establish a robust foundation for reliable and trustworthy data.
Addressing Regulatory and Security Considerations
The financial industry operates under stringent regulatory requirements. Your financial data quality management framework must address these, including data privacy and security. Implement security measures to protect sensitive data and ensure your framework aligns with relevant regulations. This protects your institution from financial and reputational damage.
Integrating Data Quality Tools
Consider using data quality tools like OpenRefine to automate and streamline processes such as data profiling, cleansing, and validation. This can improve the efficiency and accuracy of your framework, further strengthening your data quality management. Automating these tasks frees up your team to focus on strategic initiatives. By implementing these key components, your financial institution can build a robust framework for effective data quality management.
Beyond Audits: Continuous Monitoring That Catches Everything

Traditional periodic data audits aren't enough to maintain high financial data quality in today's fast-paced financial markets. Leading financial institutions are moving from reactive to proactive strategies. They're embracing continuous monitoring to ensure their data remains a trustworthy asset. Think of it like shifting from yearly health checkups to continuously tracking your vitals. This provides a constant stream of information, enabling immediate action when necessary.
Real-Time Monitoring: A Proactive Approach to Data Quality
Real-time monitoring systems transform financial data quality management. Instead of a periodic concern, data quality becomes a continuous strength. These systems constantly watch for inconsistencies and potential problems, allowing for immediate intervention. This means issues are identified and addressed before they impact business decisions or regulatory compliance.
Building Your Monitoring Tech Stack
Implementing continuous monitoring requires a robust technology stack. Automated validation tools act as the first line of defense. They instantly flag inconsistencies as they arise, much like automated proofreaders constantly scanning for errors. Intelligently designed dashboards then visualize quality trends, offering a comprehensive overview of your data's health. This visualization empowers you to identify patterns and potential risks at a glance.
Setting the Right Frequency and Thresholds
Effective monitoring requires careful consideration of frequency and thresholds. Different financial data types have different requirements. High-volume transactional data might need more frequent monitoring than static reference data. Setting appropriate thresholds minimizes false alarms while ensuring critical issues are caught. It’s similar to adjusting the sensitivity on a smoke detector. Too sensitive, and you're constantly dealing with false alarms; not sensitive enough, and you might miss a real fire.
Additionally, establishing clear benchmarks and thresholds for data quality is crucial. This practice helps define acceptable standards and triggers alerts when these standards are breached. In the financial sector, continuous data quality monitoring is crucial for successful AI and analytics initiatives. Learn more about this in the article, Data Quality Management for AI Success in 2025.
Building an Effective Alert System
A well-designed alert system is vital. Alerts should be clear, concise, and directed to the right people at the right time. This ensures prompt action and minimizes the impact of data quality issues. Think of a well-organized emergency response team: everyone knows their role and acts quickly when needed.
The Benefits of Continuous Monitoring
- Early Error Detection: Catch issues before they become major problems.
- Proactive Problem Solving: Address data quality issues proactively, minimizing their effect.
- Improved Decision Making: Rely on high-quality, real-time data for informed decisions.
- Enhanced Regulatory Compliance: Continuously monitor data to meet regulatory requirements.
By embracing continuous monitoring, financial institutions can transform their financial data quality management into a proactive strength. This ensures data remains a reliable and valuable asset.
The ROI of Getting Financial Data Quality Right
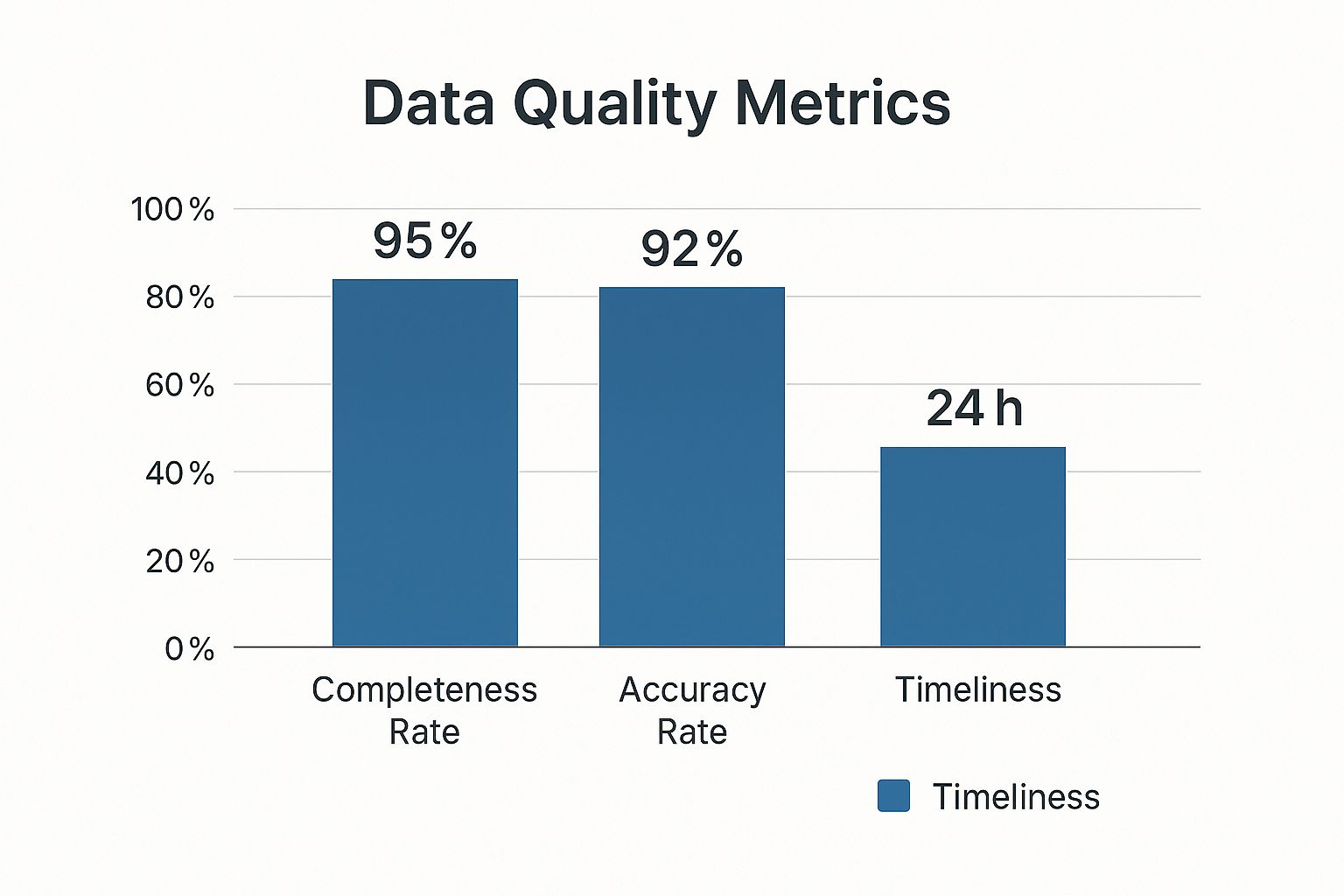
The infographic above illustrates key data quality metrics, including completeness, accuracy, and timeliness. Maintaining high standards across these metrics is crucial for reliable financial data. This, in turn, leads to better decision-making and improved financial outcomes.
Investing in financial data quality management is a strategic move with a tangible return. While the initial investment might seem substantial, the potential long-term benefits outweigh the upfront costs. Let's explore how improved data quality translates into measurable financial gains.
Quantifying the Benefits of Data Quality
Accurate, complete, and timely data positively impacts every part of a financial institution. Consider the often tedious process of reconciliation. With high-quality data, this process becomes significantly more efficient, freeing up valuable staff time for more strategic work and directly reducing labor costs.
Robust financial data quality management also minimizes the risk of compliance penalties. Errors in financial reporting, often due to poor data quality, can lead to hefty fines. Preventing these errors proactively protects your organization's reputation and strengthens its financial standing.
The increasing volume and complexity of financial data pose significant risks to data quality, impacting organizational performance. In 2024, the average global cost of a data breach reached $4.88 million, highlighting the financial consequences of poor data management. Businesses with high-quality, real-time data achieved 62% higher revenue growth and up to 97% higher profit margins than competitors. Learn more: Top Data Quality Trends for 2025.
Uncovering Hidden Costs
Beyond the readily apparent benefits, improved financial data quality management also addresses hidden costs often missed on balance sheets. These hidden costs, while less obvious, can significantly impact an organization’s bottom line.
One hidden cost is the opportunity cost of delayed insights. Poor data quality hinders timely analysis, leading to missed opportunities and slower decision-making. This can result in lost revenue and a weaker competitive edge.
Another overlooked cost is the drain on resources from manual verification. When data quality is poor, staff must spend valuable time manually verifying information, a costly and time-consuming process.
Finally, reputational damage from reporting errors can have long-term financial consequences. Inaccurate reporting erodes trust, potentially impacting investment and leading to lost business.
Building a Compelling Business Case
The benefits outlined above make a strong case for investing in financial data quality management. By quantifying the ROI and highlighting the hidden costs, you can secure buy-in and sustained investment for data quality initiatives. This means prioritizing data quality as a strategic imperative.
By connecting data quality to improved financial performance, organizations can justify the resources needed for effective financial data quality management. This investment strengthens the organization's financial foundation and contributes to long-term success.
Overcoming the Real Challenges in Financial Data Quality
Successfully managing financial data quality is crucial in today's financial landscape. While the advantages are evident, hidden challenges can impact even the most well-planned projects. Let's delve into these common obstacles and explore effective solutions.
Breaking Down Data Silos
One of the most significant hurdles is the presence of data silos. Various departments often store financial data in separate systems, leading to inconsistencies and preventing a comprehensive view. It's like trying to complete a jigsaw puzzle with pieces scattered throughout a house.
The solution? Implement a robust data integration strategy. This involves connecting these isolated data repositories and establishing a single source of truth. Standardizing data formats and implementing efficient data sharing processes across departments are also key.
Modernizing Legacy Systems
Many financial institutions still rely on legacy systems not designed for today's data demands. These outdated systems can be slow, inflexible, and challenging to integrate with modern tools, much like attempting to run the latest software on an antiquated computer.
The answer lies in modernizing these systems, either by upgrading them or migrating to more current platforms. This investment can significantly improve both data quality and operational efficiency.
Managing Resource Constraints
Limitations in both budget and personnel can restrict the scope of financial data quality projects. Prioritization is paramount.
Focus on data areas with the greatest impact on critical business decisions and regulatory compliance. Strategically allocate limited resources for maximum effectiveness. Learn more in our article about How to master financial risk management strategies.
Fostering a Culture of Data Quality
Even the most advanced technical solutions can be hindered by cultural resistance. Data quality shouldn't be seen as solely an IT issue, but as a shared organizational responsibility.
Building a data-driven culture requires training, communication, and incentives. Everyone, from entry-level employees to senior management, needs to understand the value of high-quality data. It's similar to establishing a healthy lifestyle – it takes commitment and effort from everyone involved.
Actionable Strategies for Financial Environments
These challenges require targeted solutions for specific financial sectors.
- Banking: Emphasize real-time data quality for fraud detection and regulatory reporting.
- Insurance: Prioritize accurate customer and policy data for efficient underwriting and claims processing.
- Investment Management: Ensure data integrity for precise portfolio management and performance reporting.
| Challenge | Strategy | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Data Silos | Data Integration | Implementing a central data warehouse |
| Legacy Systems | Modernization | Migrating to cloud-based platforms |
| Resource Constraints | Prioritization | Focusing on critical data domains |
| Cultural Resistance | Training & Communication | Implementing data literacy programs |
By addressing these challenges directly, financial institutions can unlock the full potential of their data. This improves decision-making, reduces risk, and provides a competitive edge. This practical roadmap offers guidance for those starting their data quality journey and those seeking to enhance existing programs. Remember, data quality isn't a one-time fix, but an ongoing process of continuous improvement.
Transformative Technologies Reshaping Financial Data Quality
The financial world thrives on data. This makes financial data quality management more important than ever. New technologies are emerging that offer innovative approaches to ensuring data accuracy and reliability. These advancements empower financial institutions to not only manage data, but also actively improve its quality. This unlocks potential for better decision-making and strategic advantages.
The Power of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are changing the game in financial data quality. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning move beyond traditional rule-based systems. They identify subtle anomalies and patterns that might otherwise be missed, much like a detective spotting tiny inconsistencies others overlook. AI and ML can similarly detect hidden data quality issues, preventing small problems from becoming major headaches.
For example, AI algorithms can analyze massive transactional datasets, flagging suspicious activity that could indicate fraud. They can also predict data quality issues based on historical patterns, allowing for proactive intervention. This lets financial institutions address these issues before they impact operations or regulatory compliance.
Blockchain: Ensuring Data Provenance and Transparency
Blockchain, the technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, is another significant development for financial data quality. Its decentralized and immutable nature improves data provenance tracking, making it easier to trace the origin and history of data. This transparency builds trust and accountability, particularly crucial in financial transactions.
Think of a meticulously maintained ledger recording every transaction detail, accessible to all authorized parties. Blockchain operates similarly, providing a secure and transparent record of data, minimizing the risk of manipulation or errors. This enhanced transparency is essential for regulatory compliance and building confidence among stakeholders.
Natural Language Processing: Extracting Value from Qualitative Data
Financial data isn't just numbers. Qualitative information, like news articles, market reports, and customer feedback, is also crucial. Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables computers to understand and analyze human language, extracting valuable insights from unstructured data sources. Natural Language Processing adds a new dimension to data analysis.
NLP can, for instance, analyze news sentiment to assess market trends or identify potential risks. It can also interpret customer feedback to better understand their needs and preferences, enabling personalized financial services. This ability to extract meaning from qualitative data provides a more complete view of the financial world.
Practical Implementation and ROI
Integrating these new technologies requires careful planning and execution. You might be interested in: How to master financial data integration. Financial institutions need to assess their existing data infrastructure, pinpoint specific data quality challenges, and choose the appropriate tools and technologies to address them. It’s crucial to manage expectations around a realistic return on investment (ROI) while implementing these changes.
Early adopters are already seeing positive results. For example, AI-powered fraud detection systems have significantly reduced financial losses. Blockchain applications have streamlined data reconciliation processes, saving time and resources. NLP tools have enhanced market analysis, leading to improved investment decisions. However, implementation has its challenges. Organizations must address data security, integration with existing systems, and the need for specialized skills.
By embracing these technologies and tackling the associated challenges, financial institutions can transform their financial data quality management into a true strategic advantage, leading to better decisions, increased operational efficiency, and improved compliance.
Creating a Culture Where Financial Data Quality Thrives
Having the best financial data quality management tools is like owning a top-of-the-line treadmill – it won't do much good if it just sits there collecting dust. Similarly, even the most advanced technology can't improve data quality on its own. It requires a supportive organizational culture where everyone is committed to using the tools effectively and prioritizing accuracy. Let's explore how successful financial institutions are transforming their cultures to make data quality everyone's responsibility.
Securing Genuine Executive Sponsorship
Real executive sponsorship goes beyond simply signing off on budgets. Leaders need to actively champion data quality initiatives and consistently communicate their importance throughout the organization. This involves more than just talk; they need to demonstrate commitment through actions. Participating in data governance committees and including data quality metrics in performance evaluations are great examples. This visible support shows everyone that data quality is a strategic priority.
Developing Cross-Functional Ownership
Clear ownership is essential, especially in hierarchical financial organizations. Establishing cross-functional teams with members from different departments (finance, operations, IT, etc.) can help. These teams should be responsible for data quality within their specific areas. Shared ownership breaks down data silos and encourages collaboration, fostering a sense of collective responsibility for data quality.
Building Data Literacy Through Training
Many data quality issues arise from a simple lack of understanding. Effective training programs can equip employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to handle data responsibly. Data literacy training should cover topics such as data entry best practices, data validation techniques, and the importance of data governance. This empowers employees to become active data stewards.
Designing Effective Incentive Structures
Recognizing and rewarding contributions to data quality reinforces its value. Incentive programs can include bonuses, promotions, or public acknowledgement for individuals and teams who demonstrate a strong commitment to data accuracy and completeness. Positive reinforcement motivates employees to make data quality an integral part of their work.
Establishing Accountability Frameworks
Accountability frameworks should focus on driving improvement, not assigning blame. Using clear metrics and reporting mechanisms allows organizations to track progress and identify areas that need attention. Regular data quality assessments help pinpoint weaknesses and provide opportunities for continuous improvement, fostering a culture of learning and growth.
Communicating the Value of Quality Data
Different stakeholders have different perspectives. Communicating the value of quality data in a way that resonates with each group is crucial. For executives, the focus might be on the return on investment (ROI) of data quality initiatives. For front-line employees, the emphasis could be on how better data makes their jobs easier. Tailoring the message ensures buy-in from everyone.
By implementing these strategies, financial institutions can create a culture where financial data quality thrives. This shift in mindset transforms data quality from a technical hurdle to a shared responsibility, ensuring that data remains a reliable and valuable asset.