7 Bank Strategic Plan Example Breakdowns for 2025
Brian's Banking Blog
A robust strategic plan is no longer an annual formality; it is the fundamental driver of resilience and growth in a volatile market. For bank executives and directors, dissecting the successful blueprints of industry leaders provides more than just inspiration. It offers a practical, data-driven playbook. This analysis moves beyond high-level summaries to provide a granular look at seven distinct strategic initiatives, from digital transformation to operational risk overhaul.
We will break down the 'how' and 'why' behind each plan, connecting strategic choices to tangible outcomes. Each bank strategic plan example serves as a case study in execution, revealing the specific tactics and frameworks that separate market leaders from the competition. For a broader understanding of how organizations develop their strategic DNA, resources on strategic planning made simple offer valuable context.
Critically, we will demonstrate how leveraging comprehensive data intelligence, like that provided by Visbanking, is the non-negotiable element that transforms a good plan into an executable, market-leading strategy. The goal is to equip your leadership team not with theoretical knowledge, but with actionable frameworks to benchmark your institution and drive decisive action. Let's examine the blueprints.
1. JPMorgan Chase Digital Transformation Strategy
JPMorgan Chase's strategic plan offers a masterclass in leveraging scale to dominate the digital banking landscape. Rather than merely adopting new technologies, the bank's strategy centers on a massive, sustained investment in building proprietary tech capabilities. This approach is a prime bank strategic plan example for institutions aiming to control their own destiny, reduce vendor dependency, and create a deep competitive moat.
The core of their strategy is to treat technology not as a cost center, but as a primary driver of business growth and efficiency. By investing over $12 billion annually in technology and employing more than 50,000 technologists, JPMorgan Chase develops solutions in-house that are precisely tailored to its operational needs and customer expectations. This vertical integration allows for faster innovation, tighter security, and a more cohesive customer experience across all platforms.
Strategic Breakdown and Implementation
JPMorgan Chase’s execution is multifaceted, targeting both internal efficiencies and external customer-facing improvements. Their strategy is not a single initiative but a portfolio of interconnected projects.
- In-house Innovation: The creation of JPM Coin, a permissioned, blockchain-based system, demonstrates their commitment to leading, not following, in financial technology. It enables instantaneous payments for institutional clients, solving a core business problem with a direct application of emerging tech.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI is not a buzzword but a foundational element integrated across the firm. For instance, its AI models analyze billions of transactions to prevent an estimated $2 billion in fraudulent activity annually, directly protecting both customers and the bank's bottom line.
- Talent as a Differentiator: By establishing partnerships like the one with Code for America, the bank actively cultivates its tech talent pipeline, ensuring it has the human capital required to execute its ambitious digital roadmap.
This visual summary highlights the immense scale of JPMorgan Chase's commitment to its technology-first strategy.
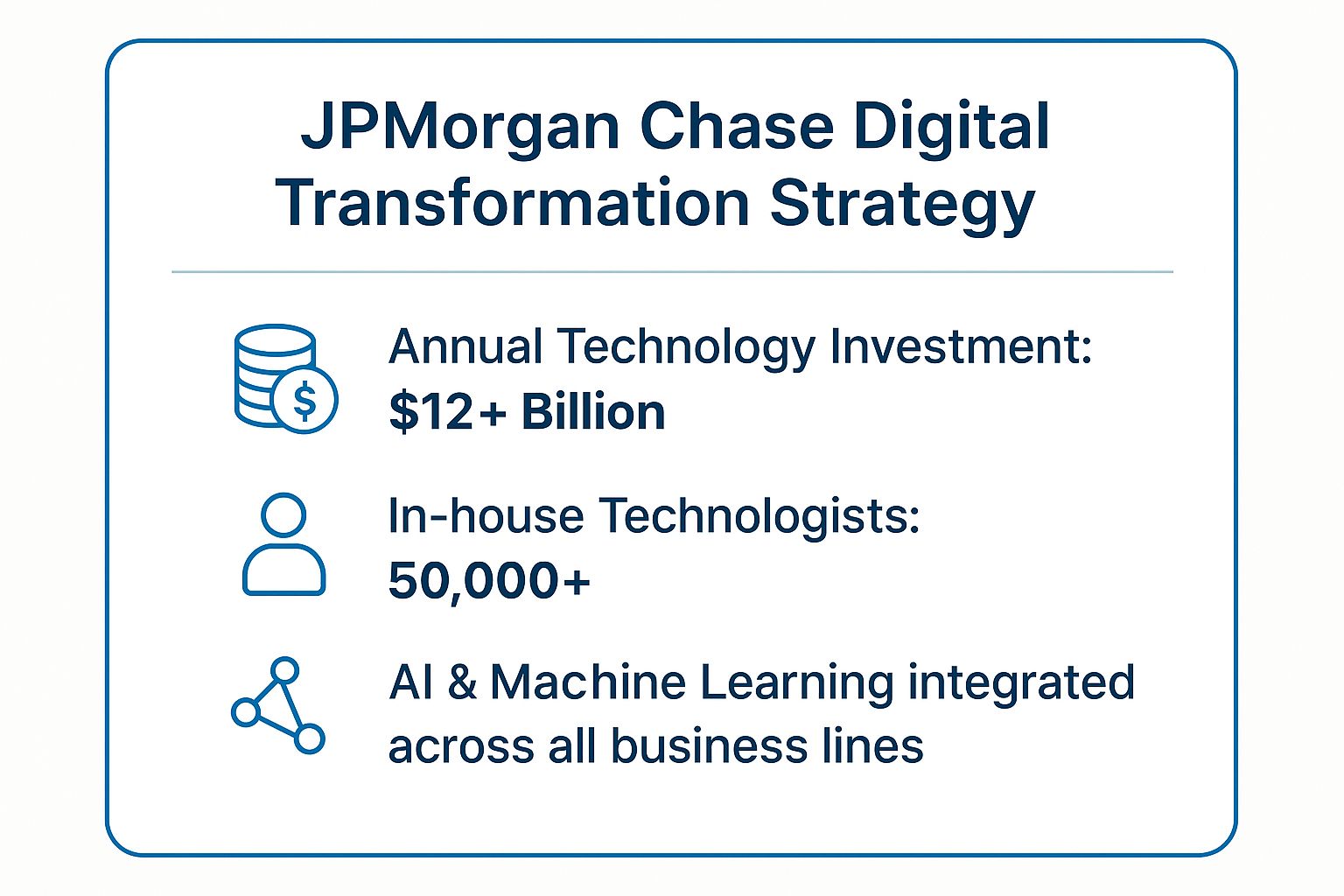
These figures underscore a critical insight: for a global financial leader, technology investment is not an optional expense but a non-negotiable component of maintaining market leadership. The sheer volume of resources dedicated to this effort makes their digital ecosystem incredibly difficult for competitors to replicate. Learn more about how to develop a comprehensive bank digital strategy.
Actionable Takeaways for Bank Executives
While most institutions cannot match JPMorgan Chase's budget, the strategic principles are scalable.
- Prioritize In-house Expertise: Identify one or two critical functions, such as data analytics or mobile app development, and invest in building an internal team rather than outsourcing. This builds long-term institutional knowledge and competitive advantage.
- Focus on Measurable ROI: Frame technology investments in terms of clear business outcomes. A data intelligence platform like Visbanking allows you to benchmark performance, showing the board, for example, that a $500k investment in a new digital onboarding platform reduced customer acquisition cost by 15% in six months compared to peers.
- Start with Customer Experience: Direct initial investments toward tangible improvements in customer-facing digital channels. A seamless mobile banking app or a faster online loan application provides immediate, visible value and builds customer loyalty.
2. Bank of America Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Strategy
Bank of America's strategic plan demonstrates how to embed Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles into the core of a financial institution's identity and operations. Instead of treating ESG as a compliance exercise, the bank has made it a central pillar of its long-term growth strategy, mobilizing immense capital and tying its brand to responsible finance. This is an essential bank strategic plan example for institutions looking to align profitability with purpose and capture the growing market for sustainable investments.
The strategy's foundation is a commitment to lead the transition to a low-carbon, sustainable economy. Bank of America’s ambitious goal to mobilize $1.5 trillion in sustainable finance by 2030 and achieve net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050 moves ESG from the periphery to the business's heart. This approach is designed to attract a new generation of investors, mitigate long-term climate risk, and create durable shareholder value.

Strategic Breakdown and Implementation
Bank of America executes its ESG strategy by integrating it across all lines of business, from capital markets to community banking. It is not an isolated initiative but a lens through which all major decisions are viewed.
- Sustainable Finance Leadership: The bank actively finances large-scale renewable energy projects and underwrites green bonds. For instance, it might lead a $500 million green bond issuance for a utility company's solar farm development, generating fees while advancing its sustainability goals.
- Product Innovation: The launch of ESG-focused investment products for wealth management clients and ESG-linked loans for corporate customers meets rising market demand. This turns a strategic priority into a tangible revenue stream.
- Operational Integration: The bank's commitment extends to its own operations through diverse supplier programs and partnerships with Community Development Financial Institutions (CDFIs). This ensures that its social and governance goals are reflected internally, not just in its external financing activities.
These initiatives show a comprehensive approach to ESG, proving that sustainable practices can drive both business and societal impact. Learn more about the critical role of ESG in the banking industry.
Actionable Takeaways for Bank Executives
While Bank of America's scale is unique, its strategic framework for ESG is highly adaptable.
- Establish Measurable Targets: Define clear, time-bound ESG goals. Instead of a vague commitment, set a specific target, such as increasing your portfolio of green-certified commercial real estate loans by 20% in three years. Use a data intelligence tool to track progress against this benchmark.
- Integrate ESG into Credit Risk: Incorporate ESG criteria into your loan approval and portfolio management processes. A data-driven approach can identify transitional risks, such as a high concentration of loans to businesses in flood-prone areas, allowing you to proactively manage portfolio-wide exposure.
- Report with Transparency: Invest in robust ESG data collection and reporting systems. Transparently communicating your progress to stakeholders, including investors and customers, builds trust and enhances your bank's reputation.
3. Goldman Sachs Consumer Banking Expansion Strategy
Goldman Sachs’ strategic pivot into consumer banking with its Marcus platform is a powerful lesson in diversification and brand leverage. Traditionally an exclusive powerhouse in investment banking, their move into the retail market demonstrates how a legacy institution can create entirely new revenue streams. This is a crucial bank strategic plan example for specialized banks seeking to reduce revenue volatility and tap into vast, underserved consumer markets.
The strategy’s brilliance lies in its digital-first, asset-light model. Instead of building physical branches, Goldman Sachs invested heavily in creating a seamless, high-value digital platform. This allowed them to enter the market with compelling offerings, like high-yield savings accounts, without the massive overhead of a traditional brick-and-mortar footprint. They leveraged their prestigious brand name to build trust quickly in a crowded field.
Strategic Breakdown and Implementation
Goldman Sachs executed this expansion through a series of calculated, high-impact moves designed for rapid market penetration and customer acquisition.
- Product-Led Growth: The initial launch of Marcus focused on a single, highly attractive product: a high-yield savings account with a rate 50 basis points higher than the national average. This simple, transparent value proposition drove rapid initial deposit growth.
- Strategic Partnerships: The collaboration with Apple to launch the Apple Card was a masterstroke. It provided immediate access to millions of loyal, tech-savvy Apple customers, dramatically accelerating their entry into the credit market and embedding their services into a major consumer ecosystem.
- Acquisition for Capability: Acquiring companies like Clarity Money (a personal finance management app) and GreenSky (a point-of-sale financing platform) allowed Goldman Sachs to quickly bolt on proven technology and established customer bases, rather than building these complex capabilities from scratch.
Actionable Takeaways for Bank Executives
While few banks have Goldman Sachs' brand recognition, the underlying strategic principles are highly replicable for institutions aiming to enter new markets or launch digital-only brands.
- Leverage an Anchor Product: Launch with one simple, best-in-class product. Use market and peer data from a platform like Visbanking to identify a gap where you can offer a rate or feature that is significantly better than the competition, creating a clear incentive for customers to join.
- Forge Ecosystem Partnerships: Identify non-financial brands with strong customer loyalty that align with your target demographic. A co-branded credit card, integrated payment solution, or embedded financing option can provide a shortcut to massive customer acquisition.
- Buy, Don't Always Build: When entering a new vertical like personal finance management or point-of-sale lending, evaluate fintech acquisition opportunities. This can drastically reduce your time-to-market and provide an immediate injection of both technology and talent.
4. Wells Fargo Operational Risk Management and Cultural Transformation Strategy
Wells Fargo's strategic response to its widespread scandals serves as a critical bank strategic plan example for any institution facing a crisis of trust. The plan moved beyond simple damage control, focusing on a fundamental rebuild of its operational risk framework and a deep-seated cultural transformation. This strategy is a powerful case study in prioritizing long-term stability and ethical conduct over short-term performance metrics.
The core of this strategy was to deconstruct and rebuild the systems that led to misconduct. Wells Fargo initiated a top-to-bottom overhaul, treating its risk and compliance functions not as secondary checks but as central pillars of the business. This involved a deliberate, multi-year investment in new leadership, simplified business models, and technology designed to enforce accountability and protect customers, fundamentally changing how the bank operates and measures success.
Strategic Breakdown and Implementation
Wells Fargo's execution was a painful but necessary journey toward rebuilding its foundation. The strategy was not a single initiative but a comprehensive program designed to address systemic failures at their root.
- Radical Leadership and Governance Overhaul: The bank brought in external leaders, including CEO Charlie Scharf, to break from past practices. This new leadership team was empowered to restructure the organization, enhance board oversight, and establish clear lines of accountability for risk management.
- Massive Customer Remediation: Wells Fargo committed over $5 billion to customer remediation programs. This was a direct, tangible action to repair harm and demonstrate a renewed commitment to fair customer outcomes, a critical step in regaining public and regulatory trust.
- Simplification of Products and Incentives: The infamous "Gr-eight" cross-selling goal was eliminated. The bank simplified its product portfolio and redesigned employee incentive structures to reward ethical behavior and positive customer outcomes, not just sales volume. This directly addressed the root cause of the fraudulent account scandal.
Actionable Takeaways for Bank Executives
The lessons from Wells Fargo's turnaround are vital for any bank, particularly for those looking to fortify their own risk and compliance frameworks before a crisis hits.
- Embed Risk in Business Strategy: Ensure that risk management is not an isolated function but an integral part of strategic decision-making. Every new product or initiative must be evaluated through a rigorous risk and compliance lens.
- Align Incentives with Customer Outcomes: Scrutinize all compensation and incentive plans. Use data to ensure they reward prudent risk-taking and long-term customer satisfaction, not just transactional metrics that could encourage misconduct.
- Invest in Proactive Monitoring: Implement robust data intelligence systems to monitor employee conduct, sales practices, and customer complaints in real-time. For example, anomaly detection algorithms can flag a branch with an unusually high rate of new account openings with minimum funding, allowing for early intervention before a problem escalates. You can learn more about how to structure a robust response with a strong foundation in banking strategic planning.
5. DBS Bank Digital Banking Innovation Strategy
DBS Bank's strategic plan is a powerful blueprint for how a traditional institution can fundamentally reinvent itself as a digital leader. Instead of simply bolting technology onto existing processes, DBS embarked on a holistic transformation guided by the mantra, "Making Banking Invisible." This approach serves as an exceptional bank strategic plan example for banks aiming to integrate digital so deeply into their operations that they function more like a technology company than a traditional bank.
The core of their strategy was to dismantle legacy systems and culture, rebuilding from the ground up with a digital-first mindset. Under the leadership of CEO Piyush Gupta, the bank systematically digitized its entire technology stack and re-engineered its processes around the customer journey. This wasn't about launching a new app; it was about embedding digital capabilities into every facet of the organization, from front-end customer interactions to back-end risk management.
Strategic Breakdown and Implementation
DBS executed its vision through a multi-pronged approach focused on technology, culture, and customer experience. The bank’s strategy was not a single project but a continuous, organization-wide movement.
- Radical Digital Transformation: The launch of "digibank" in India and Indonesia, a fully mobile-only bank, was a landmark achievement. By using AI for onboarding and verification, it acquired over 3 million customers in its first 24 months with minimal physical infrastructure.
- AI and Customer Service: DBS deployed AI-powered virtual assistants and chatbots to handle customer queries, which now manage over 80% of routine customer requests, freeing up human agents for more complex advisory roles and reducing call center costs by 30%.
- Open Banking via APIs: By creating one of the world's largest banking API marketplaces, DBS enabled third-party developers and fintechs to build new services on top of its platform. This fostered innovation and embedded DBS's services into various digital ecosystems, effectively "making banking invisible."
Actionable Takeaways for Bank Executives
While DBS's transformation was comprehensive, its core principles can be adapted by institutions of any size to drive meaningful change.
- Map and Own the Customer Journey: Use customer journey mapping to identify friction points. Data might reveal that your mortgage application abandonment rate spikes at the document upload stage. This is a specific, data-defined problem your team can solve to directly impact loan volume.
- Invest in Digital Fluency: A digital strategy is only as strong as the people executing it. Implement continuous training programs to upskill employees at all levels, ensuring they have the digital literacy and data skills needed to thrive.
- Embrace a Fintech Mindset: Establish dedicated innovation labs or "agile tribes" to rapidly prototype and test new ideas. Foster a culture that rewards experimentation and learns quickly from failures, just as a tech startup would.
6. Ant Group (formerly Ant Financial) Ecosystem Strategy
Ant Group's strategy provides a powerful fintech-driven bank strategic plan example for building a comprehensive financial ecosystem from a single, high-frequency touchpoint. By building out from its ubiquitous payment platform, Alipay, Ant created a closed-loop system that captures users and seamlessly guides them into a full suite of financial services. This model is ideal for institutions looking to leverage a strong customer base in one area to expand into new, high-growth verticals.
The core of this strategy is leveraging data to understand and serve previously ignored market segments, particularly small and micro-enterprises and individual consumers. Instead of starting with traditional banking products, Ant began with payments, a daily necessity. This generated a massive trove of transactional data, which became the fuel for developing highly targeted and accessible credit, investment, and insurance products, creating powerful network effects that are exceptionally difficult for traditional banks to replicate.
Strategic Breakdown and Implementation
Ant Group's execution relies on technology and data to create a synergistic portfolio of services, where each service strengthens the others.
- Platform-as-a-Launchpad: Alipay was the entry point. Its integration with the e-commerce giant Alibaba provided an initial user base of hundreds of millions. This foundation was then used to launch other high-value services.
- Targeted Product Innovation: MYbank was established to offer micro-loans to small businesses, using real-time payment data to make credit decisions in minutes, a process that would take traditional banks weeks. Similarly, the Yu'e Bao money market fund allowed users to invest their spare Alipay balance with a single click, democratizing wealth management.
- Data-Driven Risk Management: The creation of Sesame Credit, a proprietary credit scoring system, illustrates a core strategic pillar. It uses alternative data sources like transaction history and user behavior to assess creditworthiness for individuals who lack a formal credit history, opening up financial services to a vast, underserved population.
Actionable Takeaways for Bank Executives
While building an ecosystem on the scale of Ant Group is a monumental task, the underlying principles offer a clear roadmap for growth.
- Identify Your "Alipay": Pinpoint your bank’s most frequently used service or product. Is it your mobile app's check deposit feature or a specific type of business account? Reinforce this core offering and use it as a strategic launchpad for new, related services.
- Leverage Existing Data for New Markets: Use your internal data intelligence to identify underserved niches. Transactional data can reveal customers who might be prime candidates for small business loans, wealth management, or insurance products, even if they don't fit traditional profiles. This data-first approach is key.
- Build Partnerships to Expand Your Ecosystem: You don't need to build everything in-house. Forge strategic alliances with fintechs or other service providers to quickly add value to your platform and test new product offerings without the massive upfront investment.
7. Nubank Digital-First Neobank Strategy
Nubank’s rise provides a powerful bank strategic plan example for how to build a dominant financial institution from the ground up, entirely outside the traditional brick-and-mortar framework. The neobank’s strategy was not just to be digital, but to be digital-first, customer-obsessed, and radically transparent in a market plagued by high fees and poor service. This approach allowed Nubank to target and win over millions of underbanked and frustrated consumers in Latin America.
The core of their strategy is a relentless focus on solving customer pain points with a low-cost, technology-driven operating model. By eliminating physical branches and legacy systems, Nubank built a cost structure that allowed it to offer no-fee products, starting with its iconic purple credit card. This created a powerful value proposition that fueled rapid, organic growth through word-of-mouth marketing and brand advocacy.

Strategic Breakdown and Implementation
Nubank's execution demonstrates a masterclass in product-led growth and market expansion. The strategy unfolded in deliberate, focused phases, with each step building on the success of the last.
- Product-Led Entry: Nubank launched with a single, highly differentiated product: a no-annual-fee credit card managed entirely through a mobile app. This solved a major customer pain point in Brazil, where annual fees could reach $200, and established a strong brand reputation for fairness and simplicity.
- Ecosystem Expansion: After perfecting the credit card experience, Nubank expanded its offerings to include personal banking (NuConta), loans, and investment products. This transformed the company from a single-product fintech into a comprehensive financial platform, significantly increasing customer lifetime value.
- Geographic Scaling: Using its proven playbook from Brazil, Nubank successfully expanded into other large Latin American markets, including Mexico and Colombia. This demonstrated the scalability of its technology platform and business model across different regulatory environments.
Actionable Takeaways for Bank Executives
While building a neobank from scratch is a unique journey, the principles behind Nubank's success are highly relevant for incumbent banks seeking to innovate and capture new market segments.
- Launch a "Fighter Brand": Instead of overhauling legacy systems, consider launching a separate, digital-only brand to target a specific demographic like Gen Z. This allows you to experiment with new products and pricing models without disrupting your core business.
- Obsess Over a Single Pain Point: Identify the single biggest source of frustration for a target customer segment, such as overdraft fees or complex loan applications. Dedicate a cross-functional team to solving that one problem exceptionally well before expanding.
- Leverage Data for Simplicity: Use data intelligence platforms not just for risk assessment but to simplify the user experience. By analyzing user behavior, banks can remove unnecessary steps, streamline interfaces, and proactively offer support, turning complexity into a competitive advantage.
Strategic Plan Comparison of 7 Leading Banks
| Strategy Title | 🔄 Implementation Complexity | 💡 Resource Requirements | 📊 Expected Outcomes | 💡 Ideal Use Cases | ⭐ Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPMorgan Chase Digital Transformation Strategy | High complexity due to legacy integration and AI across lines | $12+ billion annual investment; 50,000+ in-house technologists | Competitive advantage; improved efficiency; enhanced CX | Large-scale banking tech overhaul | Technology leadership; improved risk management |
| Bank of America ESG Strategy | Moderate complexity with measurement and reporting challenges | Strong ESG data collection systems; stakeholder engagement | Enhanced brand loyalty; sustainable finance growth; compliance | Sustainable finance and social responsibility | Access to ESG markets; improved long-term risk mitigation |
| Goldman Sachs Consumer Banking Expansion | High complexity; cultural & operational shifts | Significant digital investment; fintech acquisitions | Revenue diversification; reduced earnings volatility | Entering retail consumer banking | Stable deposit funding; expanded market |
| Wells Fargo Operational Risk & Cultural Change | High complexity; time-intensive cultural transformation | Multi-billion remediation costs; governance improvements | Rebuilt trust; stronger risk controls; cultural improvements | Post-scandal risk and ethics overhaul | Rebuilt reputation; improved sustainability |
| DBS Bank Digital Banking Innovation | High complexity; fintech integration and agile practices | High tech infrastructure investment; innovation labs | Customer satisfaction increase; market share growth | Digital banking leadership | Operational cost reduction; employee engagement |
| Ant Group Ecosystem Strategy | Very high complexity managing multiple fintech ecosystem lines | Large-scale tech and data investment; regulatory compliance | Massive user base; diversified revenues; strong network effect | Tech-driven ecosystem finance | Market dominance; data-driven product development |
| Nubank Digital-First Neobank Strategy | Moderate complexity; digital-only delivery model | Scalable tech platform; heavy customer service investment | Rapid growth; high satisfaction; financial inclusion | Digital-first, underbanked markets | Low costs; customer loyalty; scalable innovation |
From Insight to Action: Activating Your Strategic Intelligence
The strategic journeys of institutions like JPMorgan Chase, DBS Bank, and even challengers like Nubank reveal a powerful, unifying truth: market leadership is no longer won by intuition alone. It is earned through the disciplined application of data intelligence to every facet of the business. From Goldman Sachs's precise expansion into consumer banking to Wells Fargo's data-driven cultural overhaul, a successful bank strategic plan example is invariably a story of data translated into decisive action.
These case studies demonstrate that a strategic plan is not a static document. It is a living framework, continuously validated and refined by real-time market signals and performance metrics. The common thread is not just having a plan, but activating it with superior intelligence.
The New Standard: From Reactive Reporting to Proactive Strategy
The era of relying on quarterly call reports and historical snapshots is over. Today’s most competitive banks operate on a cycle of continuous improvement fueled by dynamic data. The key takeaways from our analysis underscore this shift:
- Granularity Drives Growth: JPMorgan didn't just decide to "go digital." It used granular data to identify specific customer journeys and friction points to target with its digital investments, maximizing ROI. Similarly, a community bank can use a platform like Visbanking to identify underserved niches in commercial real estate or specific SBA loan categories where its peers are succeeding, turning broad strategy into targeted execution.
- Benchmarking Mitigates Risk: Wells Fargo’s recovery depended on more than new policies. It required constant benchmarking of operational risk metrics, compliance KPIs, and even employee sentiment against industry standards to prove its transformation was taking hold. This principle applies universally, whether assessing credit risk in a loan portfolio or evaluating the efficiency of a new branch model.
- Ecosystems are Built on Data: The success of DBS Bank and Ant Group was not accidental. They meticulously analyzed customer behavior data to build interconnected ecosystems that anticipate needs, creating a powerful moat against competitors. Understanding where your customers go for adjacent financial services is the first step to capturing that value yourself.
Activating Your Bank’s Intelligence
Moving from insight to action requires a fundamental shift in how your leadership team engages with information. It means replacing static reports with dynamic, query-based analysis. Instead of a simple report on your loan portfolio's growth, you should be able to instantly benchmark its performance, yield, and r