Effective Bank Financial Planning for Sustainable Growth
Brian's Banking Blog
Bank Financial Planning Essentials: Beyond the Basics

Effective bank financial planning is the foundation of a strong and successful institution. It's about strategically balancing protecting assets with pursuing growth opportunities. This careful balance is what sets thriving banks apart.
Core Components of Effective Bank Financial Planning
Successful bank financial planning relies on several interconnected parts. These elements work together to create a flexible system that can adapt to market changes.
Capital Utilization: Optimizing capital use involves strategically allocating resources to lending activities, investments, and maintaining reserves. These reserves are crucial for meeting regulatory requirements and handling unexpected market downturns.
Integrated Planning: An integrated planning framework aligns departmental budgets and strategic initiatives. It creates a clear roadmap for the bank's activities and encourages collaboration across the organization.
Dynamic Systems: Modern banks are moving towards dynamic systems that can adapt to real-time market changes. This flexibility allows institutions to quickly adjust their strategies and take advantage of new opportunities. This is in contrast to older, static planning processes.
Real-World Applications of Bank Financial Planning
These principles are being used by banks of all sizes with real results.
Smaller community banks are using these frameworks to efficiently allocate capital to local businesses and community projects. This contributes to the growth of their regional economies.
Larger institutions are using sophisticated financial planning tools to manage complex investment portfolios and navigate international markets.
Historically, economic cycles have heavily influenced banking. The 2008 financial crisis highlighted the importance of robust financial planning and risk management. Banks experienced significant declines in profitability and asset quality due to subprime lending and the resulting defaults. For more information on the current banking outlook, check out the EY Global Banking Outlook 2025.
The Future of Bank Financial Planning
The financial world is constantly changing. Bank financial planning must adapt to this ever-evolving landscape. This requires a shift from purely defensive strategies to a more proactive and strategic approach. Banks must learn to anticipate and use market changes for sustained growth and profitability. By implementing adaptable financial planning processes, banks can position themselves for success in a competitive environment.
Navigating Economic Volatility: Planning That Adapts
Economic cycles have a significant impact on the banking industry, constantly reshaping priorities and opportunities. Leading financial institutions develop bank financial planning frameworks that don't just react to these cycles, but thrive within them. By understanding these cycles, banks can identify early warning indicators and turn them into strategic advantages. This requires making key planning adjustments during different economic phases.
Recognizing Early Warning Indicators
Just like a ship's captain watches for changing weather patterns, banks must constantly monitor the economic horizon. These indicators often change depending on the specific economic phase. For example, during periods of economic growth, indicators might include rising inflation and increasing consumer debt levels.
Conversely, during an economic contraction, indicators might include declining manufacturing output and rising unemployment claims. Recognizing these indicators allows banks to anticipate changes and act proactively, rather than reactively.
Adapting to Economic Phases
This proactive approach is essential for effective bank financial planning. During periods of growth, banks might focus on expanding their lending and investment portfolios. They might also invest in new technologies and explore new market opportunities.
However, economic contractions require a different strategy. Banks may need to tighten lending standards, reduce operating costs, and strengthen risk management practices. During the recovery period, the focus often shifts to rebuilding capital reserves and supporting economic recovery through targeted lending and investments.
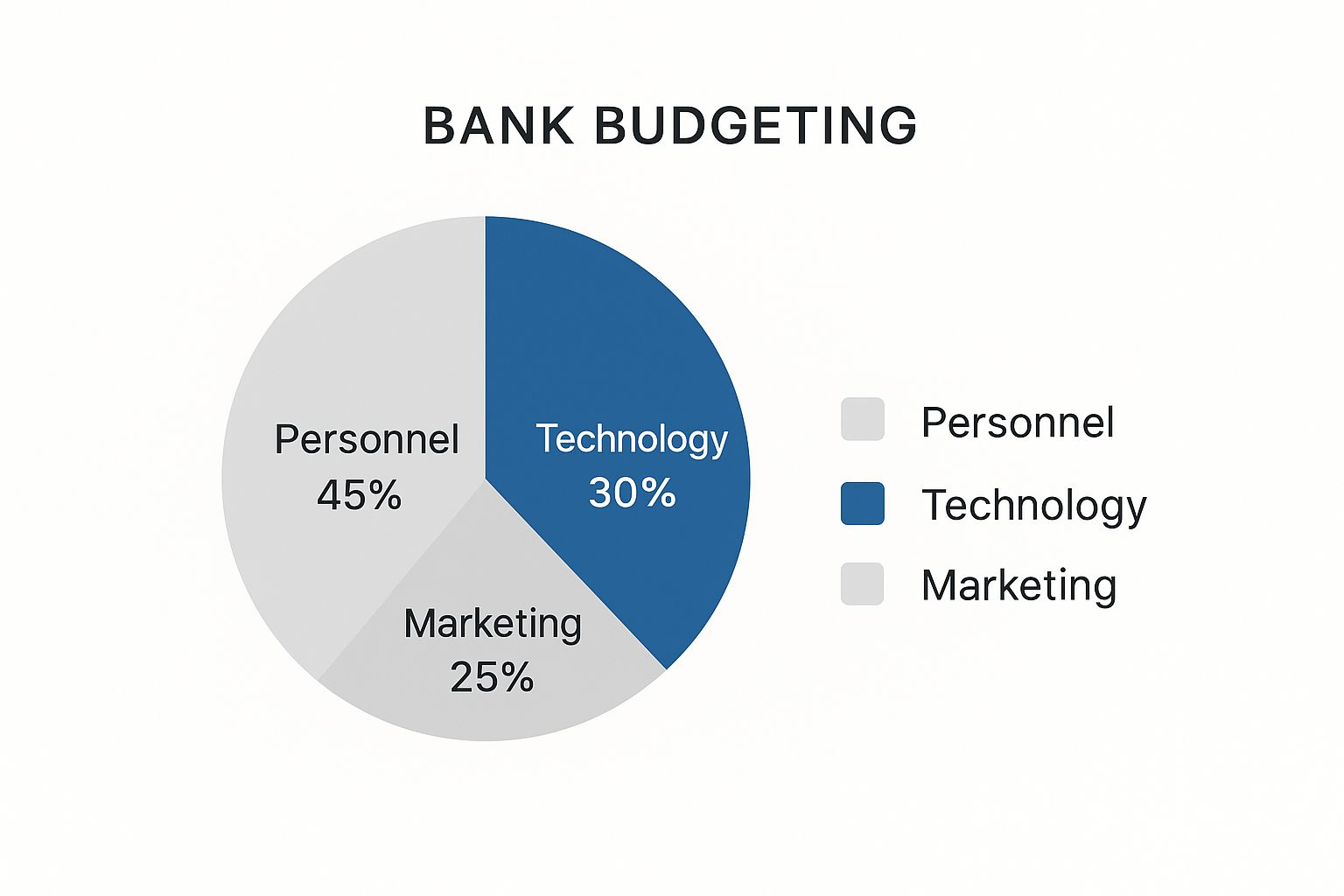
This infographic illustrates how banks typically allocate their budget across key areas: 45% for personnel, 30% for technology, and 25% for marketing. This breakdown highlights the importance of investing in both human capital and technological infrastructure, while also maintaining a focus on reaching new customers. Balancing these three budget categories strategically contributes to successful financial planning.
To further illustrate how banks adapt their strategies during different economic cycles, let's examine some key performance metrics.
| Economic Phase | Avg. Return on Equity | Capital Requirements | Risk Management Focus | Growth Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Expansion | High (10-15%) | Moderate | Controlled Growth | Aggressive Expansion |
| Contraction | Low (0-5%) | High | Preservation of Capital | Defensive, Cost-Cutting |
| Recovery | Moderate (5-10%) | Moderate | Balancing Risk & Return | Selective Growth |
This table provides a general overview of how banking performance and strategies shift across economic cycles. It's important to note that these are average ranges, and actual figures can vary significantly depending on the specific bank and economic conditions. The key takeaway is the cyclical nature of these metrics and the importance of adapting strategies accordingly.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Recent market disruptions have provided real-world examples of how effective bank financial planning can be the deciding factor between success and failure. Some banks, caught unprepared, struggled to maintain profitability during challenging economic times.
However, forward-thinking institutions, by adapting their strategies to the changing economic climate, not only weathered the storm but emerged stronger. The global banking sector is expected to maintain a stable outlook for 2025, with about 80% of banking groups having stable rating outlooks, according to S&P Global. This stability is supported by ongoing efforts to improve credit quality and manage provisioning for potential loan defaults. By learning from these real-world cases, banks can develop more robust and adaptable planning processes for the future.
Strategic Capital Allocation: Beyond Regulatory Compliance

Successfully navigating the complexities of bank financial planning involves more than just checking the regulatory compliance boxes. It requires a strategic approach to capital allocation, turning it into a true competitive advantage. This means banks must not only protect their capital, but actively put it to work for the best possible returns.
Evaluating Investment Opportunities
Top-performing banks recognize that capital allocation is about making smart choices. They carefully analyze a range of investment options, from traditional lending portfolios to technology infrastructure and strategic acquisitions. This involves a deep understanding of market trends, risk assessment, and potential returns. For example, instead of simply expanding their lending, a bank might invest in upgrading its technology to improve efficiency and enhance the customer experience.
Frameworks for Decision-Making
Effective bank financial planning relies on a solid framework for capital allocation decisions. These frameworks need to be flexible enough to adapt to market fluctuations while also allowing banks to seize growth opportunities. This might involve diversifying investments across various asset classes or using a phased approach for large-scale projects. Understanding how to navigate periods of high inflation is also crucial for planning for economic volatility. For more on this topic, see this helpful resource: Navigating Hyperinflation: 5 Lessons from History.
Stress Testing for Robustness
A vital part of strategic capital allocation is stress testing. This involves simulating different economic conditions to evaluate the strength of capital plans. Advanced stress testing methods help ensure these plans can weather tough times without overly restricting the bank's growth potential. This provides a safety net, enabling banks to make bold moves without taking on excessive risk. For further information about data-driven decision-making in banking, see Visbanking's page on banking data analytics.
Balancing Regulation and Growth
The key challenge for banks is finding the right balance between maintaining required regulatory buffers and deploying capital for maximum returns. This requires a strong understanding of both regulatory demands and market opportunities. This approach allows banks to meet their obligations while pursuing strategic initiatives. Maintaining this balance is essential for long-term success in the competitive banking industry.
Risk Management Evolution: From Defense to Strategy
Risk management in bank financial planning has grown beyond a simple safeguard. It's now a vital strategic lever that can propel success. Leading banks are incorporating advanced risk assessment and new technologies to gain a competitive advantage. This involves managing existing risks and tackling new and emerging threats.
Quantifying and Managing Traditional Risks
Progressive institutions are taking a proactive approach to quantifying and managing traditional risks. They use data-driven methods to assess and mitigate potential losses. For instance, banks use sophisticated models to predict credit defaults and better manage loan portfolios, optimizing lending practices while minimizing potential losses.
Banks are also building frameworks for emerging risks. These include challenges like climate change, cyber vulnerabilities, and geopolitical instability, which create new hurdles for bank financial planning. Institutions are developing strategies to assess and mitigate these unconventional threats to protect their assets and ensure long-term stability.
Adapting Risk Appetites in a Changing Market
Successful banks actively adjust their risk appetites. They modify their tolerance for risk based on shifting market dynamics. For example, in uncertain economic times, banks might take a more conservative stance. During periods of growth, they might accept more risk to maximize returns. This flexible approach helps maintain competitiveness while safeguarding financial health. For more information, check out this helpful resource: How to master financial risk management strategies.
Transforming Risk Data into Actionable Insights
The most effective banks are transforming raw risk data into useful insights. They utilize data analytics to uncover patterns and trends in risk data, informing strategic decisions across various areas. This makes risk management an integral part of bank financial planning, not a separate function.
To understand how risk management has evolved, let's look at the following table:
Bank Risk Management Evolution
This table tracks the transformation of risk management approaches in banking over time
| Time Period | Primary Risk Focus | Assessment Methods | Technology Integration | Strategic Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-2000s | Credit & Market Risk | Basic Statistical Models | Limited | Primarily Reactive |
| 2000s - 2010s | Operational & Liquidity Risk | Advanced Statistical Models, Stress Testing | Moderate (Spreadsheets, Databases) | Balanced Reactive & Proactive |
| 2010s - Present | Cyber Risk, Climate Risk, Reputational Risk | AI/ML, Predictive Analytics, Scenario Analysis | High (Cloud Computing, Big Data) | Primarily Proactive |
As shown in the table, the focus of risk management has broadened considerably, along with the methods and technologies used. This evolution highlights the increasing importance of proactive risk management in the banking industry.
Case Studies and Examples
Real-world examples illustrate how these strategies work in practice. Some banks have successfully reduced climate change risks by investing in renewable energy. Others have implemented strong cybersecurity defenses to protect against cyberattacks. These cases highlight how proactive risk management boosts a bank's resilience and long-term success.
The Future of Risk Management in Bank Financial Planning
Risk management is constantly evolving. As new technologies emerge and the financial landscape shifts, banks must remain adaptable and forward-thinking. This includes using artificial intelligence and machine learning (Learn more about AI) in risk assessments and creating new frameworks to manage emerging risks. By embracing these changes, banks can protect against potential losses and gain valuable insights to drive strategic planning and sustainable growth.
Technology Investment Strategy: Beyond Digital Transformation

Technology investments are crucial for bank financial planning. They offer exciting opportunities for growth but also present complex challenges. Leading banks must carefully consider which technology initiatives to pursue, balancing the needs of today with the goals of tomorrow.
Prioritizing Technology Investments
This evaluation process requires a strategic framework. Institutions need to prioritize investments across different areas.
- Core Systems Upgrades: Modernizing core banking systems can significantly improve efficiency and enable new services.
- Customer Experience Platforms: Investments in customer-facing technology can boost satisfaction and build loyalty.
- Emerging Technologies: Exploring new technologies like AI and blockchain can open doors to future opportunities.
Prioritization involves several factors. This includes assessing potential return on investment, determining the urgency of each need, and ensuring alignment with overall strategic objectives. For further insights, explore resources like How to master banking data analytics.
Measuring Technology ROI
Evaluating the return on technology investments requires a broader perspective than traditional metrics. Effective bank financial planning considers a more holistic view of ROI.
- Customer Acquisition Costs: Technology can help lower the cost of acquiring new customers.
- Operational Efficiency Gains: Automating processes with technology reduces operational expenses.
- Competitive Positioning: Strategic technology investments can give banks a competitive edge.
For instance, implementing a new digital onboarding platform might streamline the account opening process, simultaneously reducing labor costs and attracting tech-savvy customers.
Maintaining Technology Funding
Consistent funding for technology is crucial, even during periods of market fluctuation. Successful banks create strategies to ensure continuity in essential technology initiatives while remaining flexible and adaptable to new opportunities. Effective risk management is also paramount in bank financial planning. Understanding the sources of potential loss, such as the financial risk associated with reversible payments, is critical for sound financial planning.
Balancing Short-Term Needs and Long-Term Vision
Finding the right balance between immediate operational needs and long-term transformation objectives is a key aspect of bank financial planning. This often means making careful choices between investing in quick wins versus establishing the foundation for future innovation. A bank might, for example, choose to implement a short-term fix for a legacy system while also exploring a more comprehensive, long-term solution. This balanced approach ensures both current functionality and the ability to adapt to future demands.
Building Sustainable Profitability: The Comprehensive Approach
Bank financial planning now demands more than simply reacting to market fluctuations. It requires building a strong, adaptable strategy designed for long-term profitability. This means looking past traditional interest income and discovering diverse avenues for generating revenue. It also calls for carefully balancing efficiency with strategic investment.
Diversifying Revenue Streams
Successful banks recognize the value of diversified income streams. They're moving beyond relying solely on interest income and actively pursuing fee-based services. This approach helps maintain profitability even when interest rates are volatile. For instance, many banks now provide wealth management services, investment advisory services, and other fee-based products.
Balancing Efficiency and Investment
Sustaining profitability requires a strategic balancing act. Banks must implement cost controls but also invest wisely for future growth. This means avoiding shortsighted cost-cutting measures that could jeopardize long-term success. It's about finding efficiencies that actually promote, rather than hinder, growth. Investing in technology, for example, can automate tasks, ultimately reducing costs while simultaneously improving customer service. Check out our guide on bank growth strategies for a more detailed look at this topic.
Setting Realistic Profitability Targets
Establishing achievable profitability targets is critical for effective bank financial planning. These targets should be specific to each business unit within the bank, reflecting the unique opportunities and challenges of each division. This targeted approach enables a more accurate performance assessment and more strategic resource allocation. It’s not about comparing yourself to competitors; it's about measuring progress toward specific internal objectives.
Tracking Performance Against Strategic Objectives
Leading financial institutions track their performance against well-defined strategic objectives. This goes beyond simply benchmarking against industry peers. It focuses on how effectively the bank executes its own unique strategic plan. This provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of various initiatives and offers a clearer path forward. Focusing on internal goals and execution creates a more proactive and adaptable approach to financial planning.
Developing an Integrated Financial Planning Process
An integrated financial planning process connects all the pieces. It unites all the elements—from diversifying revenue to tracking performance—into a cohesive, adaptable system. This builds institutional resilience, allowing banks to maximize growth opportunities regardless of market conditions. This proactive approach helps banks shape their future instead of simply reacting to the market. This comprehensive approach to bank financial planning is vital for navigating today's complex financial environment. By focusing on these key elements, banks can build sustainable profitability models and flourish in any market.
Ready to improve your bank's financial planning process? Visit Visbanking today to learn more about how our Bank Intelligence and Action System (BIAS) can help your institution achieve sustainable growth and profitability.